2.5 Solving Equations by Factoring
2.5.1 Prep
A. Factor the polynomials using the greatest common factor (GCF) or grouping method.
- [latex]10y^2+10[/latex]
- [latex]3t^2+6t[/latex]
- [latex]15x^2-21x^5[/latex]
- [latex]24x^4+30x^7[/latex]
- [latex]6x^2-24x+30[/latex]
- [latex]8x^3+12x^2-10x[/latex]
- [latex]15xz+20x+6yz+8y[/latex]
- [latex]24x^3-42x^2+20x-35[/latex]
- [latex]3x^2y-6x^2-3xy+6x[/latex]
- [latex]30x^2+9xy-20x-6y[/latex]
- [latex]56x^2+24xy-70x-30y[/latex]
- [latex]8xy+12x-10y-15[/latex]
B. Factor the trinomials completely.
- [latex]x^2-6x+8[/latex]
- [latex]x^2-14x-15[/latex]
- [latex]x^2+3x-28[/latex]
- [latex]x^2-6x+9[/latex]
- [latex]x^2+3x-10[/latex]
- [latex]x^2-2x-15[/latex]
- [latex]7x^2-42x+35[/latex]
- [latex]3x^2+6x-24[/latex]
- [latex]6x^2+x-2[/latex]
- [latex]5x^2-14x+8[/latex]
- [latex]9x^2+9x-10[/latex]
- [latex]7x^2+16x-9[/latex]
- [latex]8x^2+6x-9[/latex]
- [latex]10x^2+19x+7[/latex]
- [latex]3x^2-5x-2[/latex]
- [latex]12x^2+x-6[/latex]
C. Factor the binomials completely.
- [latex]x^2-49[/latex]
- [latex]4x^2-81[/latex]
- [latex]x^2+9[/latex]
- [latex]32x^3-2x[/latex]
- [latex]25x^2+100[/latex]
- [latex]49-x^2[/latex]
- [latex]x^3-x[/latex]
- [latex]3x^3-12x[/latex]
2.5.2 Preview
Example
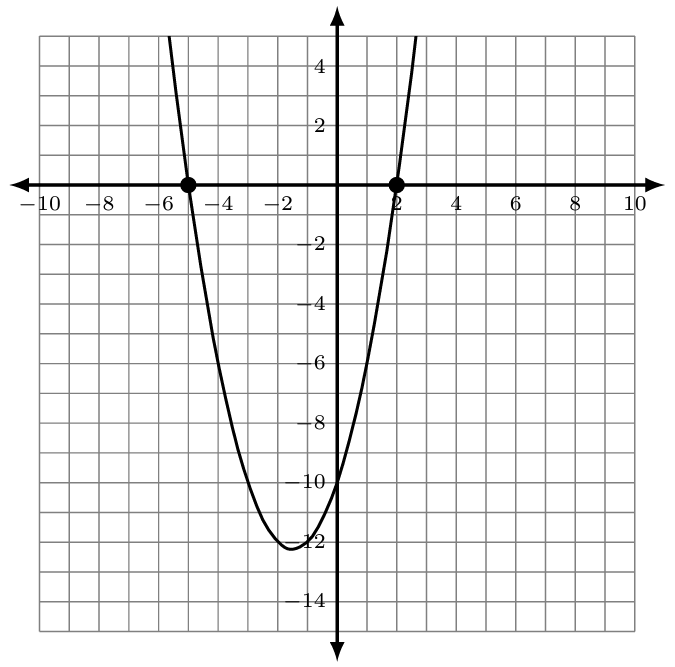
The graph of [latex]f\left(x\right)=x^2+3x-10[/latex] is shown. Notice that the x-intercepts occur at [latex]\left(-5,0\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(2,0\right)[/latex]. We can use the x-intercepts to write the factored form of this quadratic function by moving the x-intercept over to the other side.
[latex]\begin{array}{rclcccc}x&=&-5&&&&&&&&&&x&=&2\\[1em]x+5&=&-5+5&&&&&&&&&&x-2&=&2-2\\[1em](x+5)&=&0&&&&&&&&&&(x-2)&=&0\end{array}[/latex]
Multiply the factors and combine like terms.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}0&=&(x+5)(x-2)\\0&=&x^2-2x+5x-10\\0&=&x^2+3x-10\\f(x)&=&x^2+3x-10\end{array}[/latex]
Example
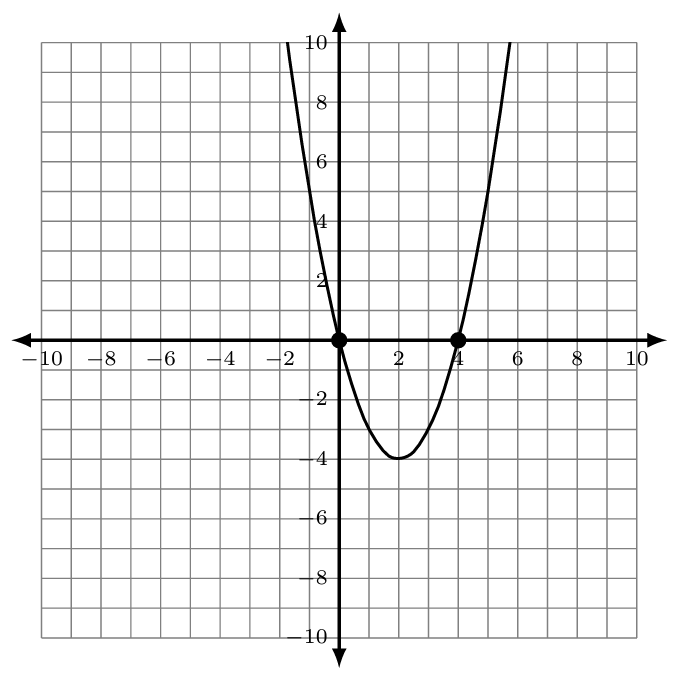
The graph of [latex]f\left(x\right)=x^2-4x[/latex] is shown. Notice that the x-intercepts occur at [latex]\left(0,0\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(4,0\right)[/latex]. We can use the x-intercepts to write the factored form of this quadratic function.
[latex]\begin{array}{rclcccc}x&=&0&&&&&&&&&&x&=&4\\[1em]x-0&=&0-0&&&&&&&&&&x-4&=&4-4\\[1em]x&=&0&&&&&&&&&&(x-4)&=&0\end{array}[/latex]
Multiply the factors and combine like terms.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}0&=&x(x-4)\\0&=&x^2-4x\\f(x)&=&x^2-4x\end{array}[/latex]
Try It!
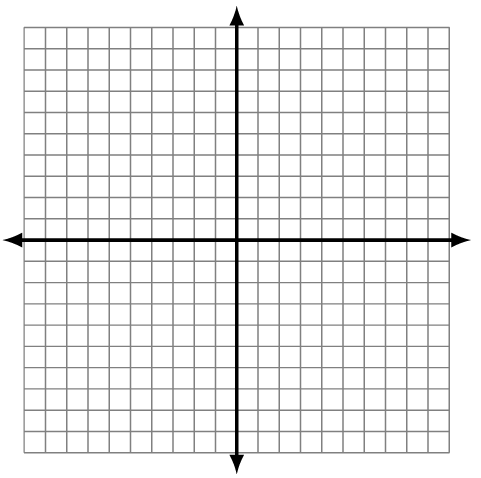
Sketch a possible graph for the quadratic function given in factored form.
[latex]f\left(x\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)[/latex]
Try It!
Sketch a possible graph for the quadratic function given in factored form.
[latex]f\left(x\right)=\left(x+6\right)\left(x-6\right)[/latex]

Example
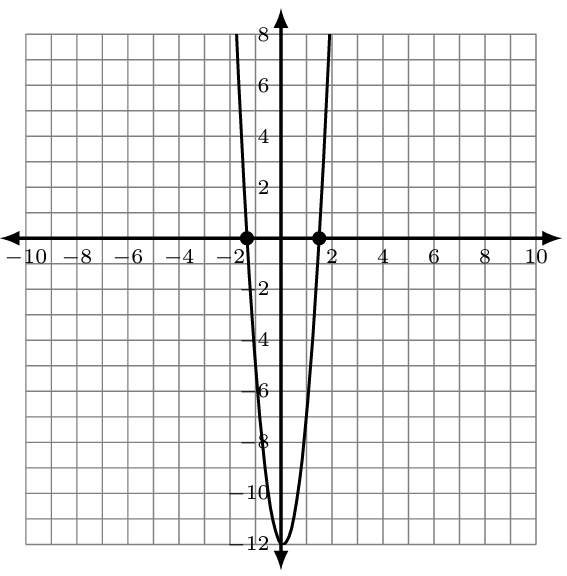
The graph of [latex]f\left(x\right)=6x^2-x-12[/latex] is shown. The x-intercepts occur at [latex]\left(\frac32,0\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(-\frac43,0\right)[/latex]. We can the x-intercepts to write the factored form of this quadratic function.
[latex]\begin{array}{rclcccc}x&=&\frac32&&&&&&&&&&x&=&-\frac43\\[1em]2⋅x&=&\cancel2⋅\frac3{\cancel2}&&&&&&&&&&3⋅x&=&\cancel3\cdot\left(-\frac4{\cancel3}\right)\\[1em]2x&=&3&&&&&&&&&&3x&=&-4\\[1em]2x-3&=&3-3&&&&&&&&&&3x+4&=&-4+4\\[1em](2x-3)&=&0&&&&&&&&&&(3x+4)&=&0\end{array}[/latex]
Multiply the factors and combine like terms
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}0&=&(2x-3)(3x+4)\\0&=&6x^2+8x-9x-12\\f(x)&=&6x^2-x-12\end{array}[/latex]
2.5.3 Classwork
A. Solve using the Zero Factor Property.
- [latex]9x^2-16=0[/latex]
- [latex]x^2+8x+16=9[/latex]
- [latex]2x^2+5=2-7x[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{x^2}9+1=\frac{2x}3[/latex]
- [latex]20x^2+4x^3+25x=0[/latex]
- [latex]2t^2+18t+36=0[/latex]
- [latex]10x^2=5x[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{x^2}5+\frac x4=\frac3{10}[/latex]
- [latex]25x^2+45x+8=0[/latex]
- [latex]3x^2-12=0[/latex]
- [latex]\frac12x^2-32=0[/latex]
- [latex]16t^2=49[/latex]
- [latex]6=11x-4x^2[/latex]
- [latex]15x^2+43x+30=0[/latex]
- [latex]2x^2=3x+35[/latex]
- [latex]6t^2+7t-24=0[/latex]
- [latex]12x^2-32x-75=0[/latex]
- [latex]30x^3-2x^2-4x=0[/latex]
- [latex]4x^2-31x=-21[/latex]
- [latex]80x^3-60x^2-90x=0[/latex]
- [latex]15t^2-t-2=0[/latex]
- [latex]12x^2+x=6[/latex]
- [latex]7x^2-23x+6=0[/latex]
- [latex]6x^2+25x+4=0[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{9x^2}{16}-\frac19=0[/latex]
- [latex]\frac14x^2=1[/latex]
B. Graph and identify the following characteristics for the function.
-
-
[latex]g\left(x\right)=2x^2+8x[/latex]
Opens: Up / Down
Axis of Symmetry:
Vertex:
y-intercept:
x-intercept(s):
Domain:
Range:
-
C. Answer the following.
- The height h (in feet) of a small rocket t seconds after it is launched is given by the function [latex]h\left(t\right)=-16t^2+128t.[/latex]
- How long is the rocket in the air?
- When is the rocket 112 feet high?
- Use the equation [latex]3x^2+9x=0[/latex] to answer the following.
- Solve using the Quadratic Formula.
- Solve using the Zero Factor Property.
- Discuss the differences between (a) and (b). State which method you prefer and why.
- Spot the error and correct it.[latex]4x^2+12x+9=0[/latex][latex]4(x^2+12x+9)=0[/latex]
2.5.4 Homework
A. Solve using the Zero Factor Property.
- [latex]x^2+8x+15=0[/latex]
- [latex]4t^2-25=0[/latex]
- [latex]6x^2-x=15[/latex]
- [latex]10x^2+100x=0[/latex]
- [latex]4t^2+12t+9=0[/latex]
- [latex]4x^2=23x+6[/latex]
- [latex]x^2+\frac{16}9=\frac83x[/latex]
- [latex]\frac12x^2-\frac56x-2=0[/latex]
- [latex]x^3+4x^2-12x=0[/latex]
- [latex]\frac32x^2+3x+\frac43=0[/latex]
- [latex]20x^2-4x=0[/latex]
- [latex]\frac29t^2+t+1=0[/latex]
- [latex]5t^2-23t+12=0[/latex]
- [latex]36x^3=81x[/latex]
- [latex]6x-4x^3=23x^2[/latex]
- [latex]5-2x^2-3x=0[/latex]
- [latex]4x^2-x[/latex]
- [latex]2x^2-50[/latex]
- [latex]\frac52t^2-\frac13t-\frac43=0[/latex]
- [latex]\frac13x^2+\frac7{12}x=\frac58[/latex]
- Give an equation you prefer to solve using the Zero Factor Property. Give an equation you prefer to solve by the Quadratic Formula.
B. Graph and identify the following characteristics for the function.
-
[latex]m\left(x\right)=-x^2+1[/latex]
Opens: Up / Down
Axis of Symmetry:
Vertex:
y-intercept:
x-intercept(s):
Domain:
Range:

C. Answer the following.
- A rocket carrying fireworks is launched from a hill above a lake. The rocket will fall into lake after exploding at its maximum height. The rocket’s height above the surface of the lake is given by [latex]h\left(t\right)=-16t^2+64t+80[/latex], where h is in feet and t is in seconds.
- How long will it take for the rocket to hit 128 feet?
- After how many seconds after it is launched will the rocket hit the lake?
- Fill in the blank to create an equation that may solved using the Zero Factor Property.
[latex]x^2+\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\;x-12=0[/latex]
- Explain in your own words how to solve the following equation using the Zero Factor Property. Be sure to explain why you perform each step.
[latex]x^2+12x+20=4x+5[/latex]

