Linear Relationships and Functions
Prep for Percent and Proportion
- [latex]\frac18[/latex]
- [latex]\frac38[/latex]
- [latex]\frac68;\;\text{equivalent}\;\text{to}\;\frac34[/latex]
- [latex]\frac26[/latex]
- [latex]\frac23[/latex]
- [latex]\frac34;\;\text{equivalent}\;\text{to}\;\frac68[/latex]
- [latex]1\frac23[/latex]
- Answers may vary.
- It is necessary to write 1 if it is the part (not the whole) in a ratio.
- Part = 8; Whole = 22.58; Fraction [latex]=\frac8{22.58}[/latex]
- Part = 58; Whole = 82; Fraction [latex]=\frac{58}{82}[/latex]
- Part = 4,630; Whole = 15,435; Fraction [latex]=\frac{4,630}{15,435}[/latex]
- Part = 212; Whole = 802; Fraction [latex]=\frac{212}{802}[/latex]
- Part = 170; Whole = 950; Fraction [latex]=\frac{170}{950}[/latex]
- Part = [latex]2\frac12[/latex]; Whole = [latex]5\frac34[/latex]; Fraction [latex]=\frac{2{\displaystyle\frac12}}{5{\displaystyle\frac34}}[/latex]
-
- subtraction
- multiplication
- division
- addition
- multiplication
- addition (-7) or subtraction (7)
- division
- multiplication
- multiplication and division
- multiplication
- multiplication and division
- multiplication and division
-
- subtraction
- subtract 5 from both sides; [latex]x=14[/latex]
- [latex]x=55[/latex]
-
- addition
- add 5 to both sides; [latex]x=7[/latex]
- [latex]x=42[/latex]
-
- division
- divide both sides by 3; [latex]x=21[/latex]
- [latex]x=22[/latex]
-
- No. [latex]x-3[/latex] is held by subtraction;
[latex]-3x[/latex] is held by multiplication - add 3 to both sides; [latex]x=15[/latex]
- divide both sides by [latex]-3;x=-4[/latex]
- No. [latex]x-3[/latex] is held by subtraction;
-
- division
- multiplication
- multiply both sides by 4; [latex]x=60[/latex]
- [latex]x=100[/latex]
- multiplication, division; division, multiplication; [latex]x=25[/latex]
- multiplication; [latex]x=\frac15[/latex]
- [latex]x=20[/latex]
- [latex]p=0.1[/latex]
- [latex]n=150[/latex]
- [latex]x=5200[/latex]
- [latex]x=17.5[/latex]
- [latex]x=21[/latex]
- [latex]x=56[/latex]
- [latex]t=20.4[/latex]
- [latex]x=4[/latex]
- [latex]x=3[/latex]
- [latex]b=8[/latex]
Classwork: Percent and Proportion
- Explain.
- Explain.
- 70
- 17.5%
- 62.5
- 130
- [latex]233.\overline3[/latex]
- 555 students
- 3.6%
- 6.97%
- 66 beats
- 800 calories
- 105.86 gallons
- $209,300
- $21.22
- $1966.67
- 62% decrease
- 25% increase
- 2 gal of 50%; 4 gal of 75%
- 4 cups; 5%
- [latex]3\frac14[/latex] cups of 2.77% fat
- 35 pints; 5% salinity
- 5 liters of 1%; The mixture is 1.57%
- [latex]\approx0.96\%[/latex]
- 2,250 people
- 1,600 trout
- $44.56
- [latex]\approx67.07\%[/latex]
- 52 games
Homework: Percent and Proportion
- [latex]10.08[/latex]
- [latex]92[/latex]
- [latex]\approx31.48\%[/latex]
- [latex]3.12[/latex]
- Explain.
- 1,234 students
- [latex]\approx71.4\%[/latex]
- An equation in which two ratios (fractions) are set equal
- Cross multiply and solve for the unknown
- [latex]t=20.4[/latex]
- [latex]x=4[/latex]
- [latex]x=3[/latex]
- [latex]k=3[/latex]
- [latex]b=8[/latex]
- 3.75 miles
- [latex]$219,000[/latex]
- [latex]3\frac13[/latex] hours
- 3,750 penguins
- 2.1 lbs
- 462 lbs
- 7,700 lbs
- 165 calories
- 19 ft
- 35 puppies, 20 adult dogs
- 630 frat men
- 51.3% are females
- [latex]$369.52[/latex]
- $9.90 discount, $23.09 sale price
- $92.81 tax, $1,217.81
- $7.00 tip
- 49% decrease
- Explain
- 4,000 gallons; 2.625% salinity
- [latex]2\frac12[/latex] cup of 4% fat
- [latex]1\frac34[/latex] cups; 1.7% alcohol
- 3 quarts of whole milk; the mixture is 5.8% fat
- liters of 1% low-fat; 1.8% fat in the mixture
Prep for Scientific Notation and Conversions
- [latex]10[/latex]
- [latex]100[/latex]
- [latex]10,000[/latex]
- [latex]10,000,000[/latex]
- Discussion may vary
- [latex]10^4[/latex]
- [latex]10^8[/latex]
- [latex]0.1[/latex]
- [latex]0.01[/latex]
- [latex]0.0001[/latex]
- [latex]0.0000001[/latex]
- Discussion may vary.
- [latex]10^{-5}[/latex]
- [latex]10^{-9}[/latex]
- [latex]700[/latex]
- [latex]0.0003[/latex]
- [latex]7,450,000[/latex]
- [latex]0.000314[/latex]
Classwork: Scientific Notation and Metric Conversions
Scientific Notation
- [latex]3.54\times10^7[/latex]
- [latex]9.876\times10^{-9}[/latex]
- [latex]2,320,000[/latex]
- [latex]0.0052[/latex]
Metric System Conversions
- [latex]0.5[/latex] m
- [latex]8,000[/latex] g
- [latex]9100[/latex] L
- [latex]98[/latex] mg
- [latex]0.0091[/latex] L
- [latex]720,000[/latex] mm
- [latex]568,000[/latex] mg
- [latex]98,000[/latex] µg
- [latex]2,000,000[/latex] µg
- [latex]40,000[/latex] cm2
- [latex]250,000,000[/latex] cm3
- [latex]130,400[/latex] km2
Homework: Scientific Notation and Metric Conversions
- [latex]3.04\times10^3[/latex]
- [latex]-4.789\times10^{-3}[/latex]
- [latex]7.18\times10^{-6}[/latex]
- [latex]3.108\times10^{6}[/latex]
- Many answers are possible.
-
- [latex]2.5\times10^{-3}[/latex]
- [latex]2.5[/latex] mg
- [latex]2500[/latex] µg
- Discuss.
- [latex]5\times10^2[/latex] mL
- [latex]1.6\times10^2[/latex] mm
- [latex]1.04\times10^7[/latex] cm
- [latex]4.8\times10^2[/latex] cm2
- [latex]1.98\times10^{-3}[/latex] kg
- [latex]2.5\times10^{-2}[/latex] km
- [latex]1.6\times10^5[/latex] mm3
- [latex]1.2\times10^{-5}[/latex] ML
- France by [latex]136,033[/latex] km2
Prep for Imperial Conversions
- [latex]90[/latex]
- [latex]19.3548[/latex]
- [latex]12,096[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{5}{8}[/latex] or 0.625
- Compare with a classmate
- [latex]\frac{\cancel8}1\cdot\frac5{\cancel8}=5[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{\cancel{4.5}}1\cdot\frac7{\cancel{4.5}}=7[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{\cancelto{2}{10}}{1} \cdot \frac{3}{\cancel5} = 6[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{\cancelto{2}{12}}{1} \cdot\frac{\bcancel5}{\cancel6}\cdot\frac7{\bcancel5}=14[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{15}{\cancel8}\cdot\frac{\cancel8}{\bcancel7}\cdot\frac{\bcancel7}4=\frac{15}4[/latex]
- [latex]\frac91\cdot\frac21\cdot\frac{11}1=198[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{\cancel9}1\cdot\frac{10}{\cancel3}\cdot\frac5{\cancel3}=50[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{\cancel{25}}4\cdot\frac2{\cancel5}\cdot\frac2{\cancel5}=1[/latex]
- [latex]72[/latex] yd
- [latex]74[/latex] feet
- [latex]64[/latex] m2
- [latex]312[/latex] ft2
- [latex]125[/latex] in3
- [latex]936[/latex] ft3
- 1; 2 (square units); 3 (cubic units)
| Length (distance) 1 dimension |
Area 2 dimensions |
Volume 3 dimensions |
Mass | Time | Imperial (British) | Metric | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. cm | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 2. cm3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 3. in2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 4. g | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 5. hm | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 6. dag | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 7. years | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 8. dL | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 9. dam2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 10. mm3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 11. m | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 12. mi | ✓ | ✓ |
- [latex]\frac{2.54\;cm}{1\;\text{in}},\;\text{length}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{12\;\text{in}}{1\;ft},\;\text{length}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{0.3048\;m}{1\;ft},\;\text{length}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{640\;\;\text{acres}}{1\;mi^2},\;\text{area}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{0.001\;m^3}{1L},\;\text{volume}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{3\;ft}{1yd},\;\text{length}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{9\;ft^2}{1yd^2},\;\text{area}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{29.5735\;cm^3}{1\;oz},\;\text{volume}[/latex]
Classwork: Imperial Conversions
- Answers may vary.
- Answers may vary.
- 2 yds
- 54.61 cm
- 131.23 yd
- 88,513.92 m
- [latex]8.0645[/latex] cm2
- [latex]46,609.2[/latex] ft2
- 13056 oz
- 6 lbs
- [latex]864[/latex] in3
- 259,200 sec
- 6 years 3.34 months
- 120 mi/day
- 272.19 L/hr
- [latex]2.998\times10^8[/latex] m/sec
- Discuss with a classmate.
Applications of Conversions
- [latex]1.58\times10^9[/latex] sec
- [latex]226.04[/latex] ft2
- [latex]2.58[/latex] sec
- [latex]1,728[/latex] in
- [latex]15,840[/latex] in2
- [latex]7.33[/latex] ft/s
- Mat’s bathtub fills faster
- 7 lb, 10.05 oz
Homework: Imperial Conversions
- [latex]6.21[/latex] mi
- [latex]120,000,000[/latex] µg
- [latex]12,672[/latex] ft
- [latex]109.68[/latex] cm2
- [latex]804.4[/latex] mL
- [latex]2[/latex] ft
- [latex]10.57[/latex] pt
- [latex]25.4[/latex] cm
- [latex]20[/latex] lb
- [latex]525,600[/latex] min
- [latex]131.234[/latex] yd
- [latex]66,908,160[/latex] ft2
- [latex]23,562[/latex] in3
- [latex]5,297.2[/latex] ft3
- [latex]4.299[/latex] lb
- [latex]42.33[/latex] oz
- [latex]4.23[/latex] pt
- [latex]220.98[/latex] m
- [latex]25.1[/latex] gal
- [latex]26.82[/latex] m/s
- [latex]5.93\times10^{-6}[/latex] m3
- [latex]0.0283[/latex] m3
- [latex]14.2[/latex] mg/mm2
- [latex]82.4[/latex] mg/mm2
- [latex]6.214[/latex] miles
- Explain.
-
- No
- Explain.
- 27.8 mph
- [latex]290.8[/latex] mph
- [latex]750[/latex] mph
- [latex]320,544[/latex] in/wk
- [latex]{5.407\times10}^{-4}[/latex] kg/s
-
-
- centimeters
-
- [latex]452.23[/latex] km
- 7 lb, 11 oz
- [latex]\approx[/latex] 54 yr, 9.5 months
- 31.7 years old
-
- 300 feet and
- 91,744 cm
- The gallon size because it is $0.02/oz.
- [latex]125,840[/latex] ft
- 53 days
- Houston by 419.58 km2
- [latex]3.73\times10^{17}[/latex] m3; [latex]3.73\times10^{20}[/latex] liters
- 31,709.8 years old
- 946,352.9 pages
- 187.96 cm
- 3 ft
- 20.86 in
- 25.4 kg
- 4 times
- 4.93 mL
- 14.79 mL
- 12.25 lbs, 5.56 kg
- 160 oz
- 4731.76 mL
- 2.464 cc
- 0.125 qt
- 50000 µg
- 2.5 cc
- 6 tsp
Prep: Linear Graphs - Intercepts Method
-
- I and IV; I and III
- I and II; III and IV
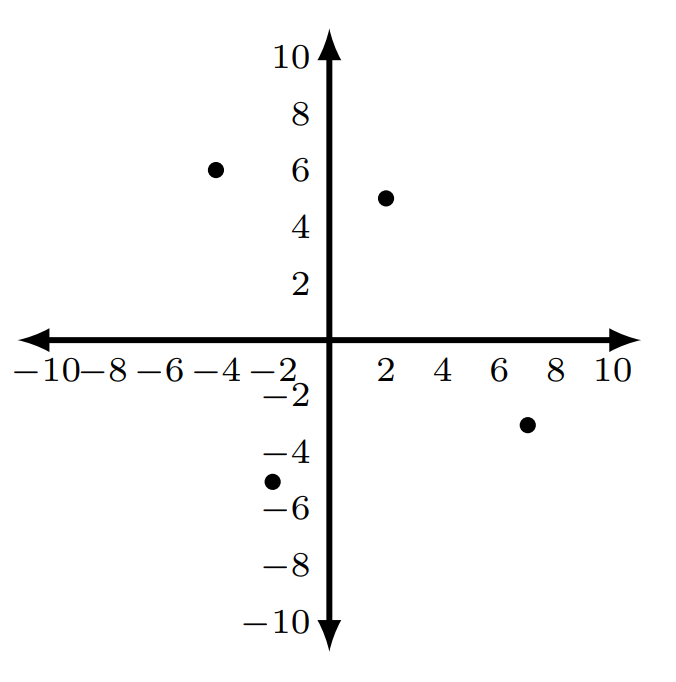
-
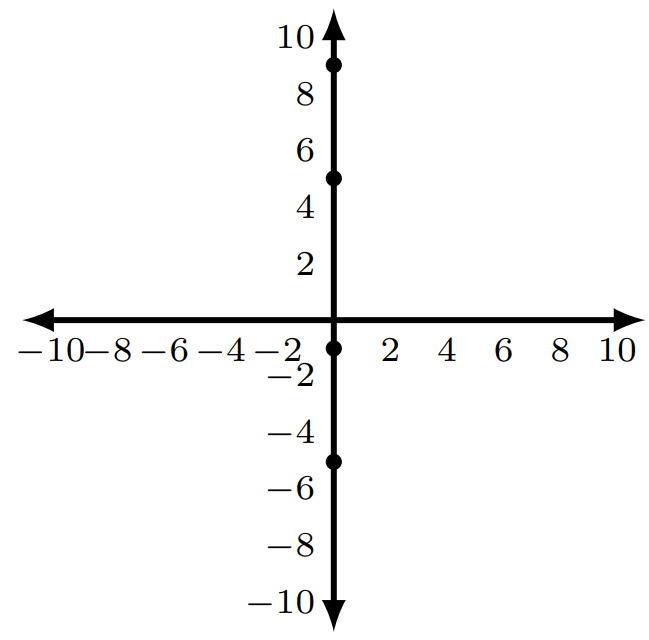
- They lie on the y-axis.
-
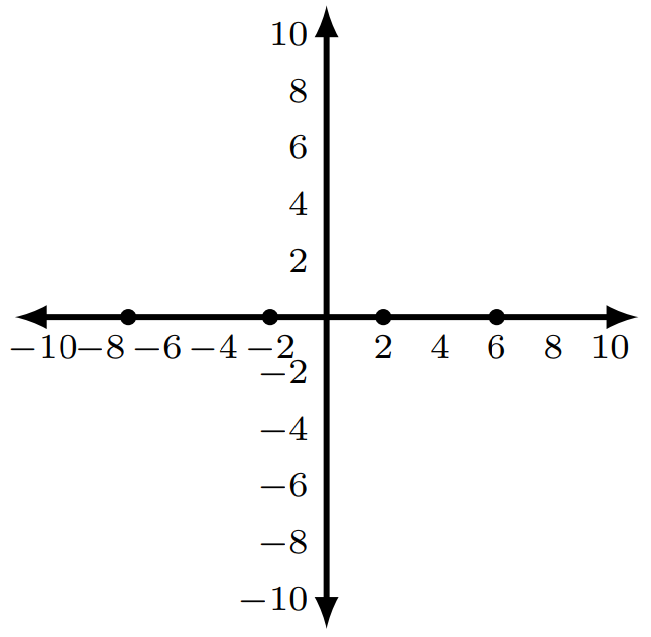
- They lie on the x-axis.
Classwork: Intercepts Method
- y-intercept: [latex](0, 9)[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](\frac{9}{2}, 0)[/latex]
- y-intercept: [latex](0, 6)[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](-6, 0)[/latex]
- y-intercept: [latex](0, \frac{1}{2})[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](-3, 0)[/latex]
- y-intercept: [latex](0, \frac{17}{5})[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](\frac{17}{8}, 0)[/latex]
- Answers may vary.
- y-intercept: [latex](0, 4)[/latex]; x-intercept: none
- y-intercept: none; x-intercept: [latex](-2, 0)[/latex]
- Answers may vary.
- y-intercept: [latex](0, 5)[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](2, 0)[/latex]
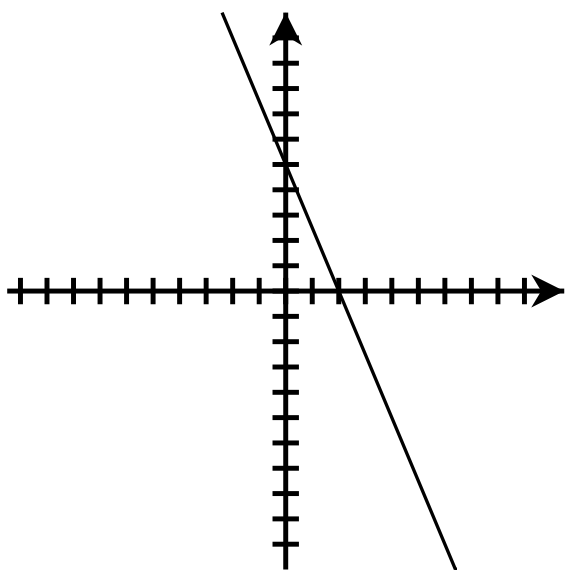
- y-intercept: [latex](0, 2)[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](-4, 0)[/latex]
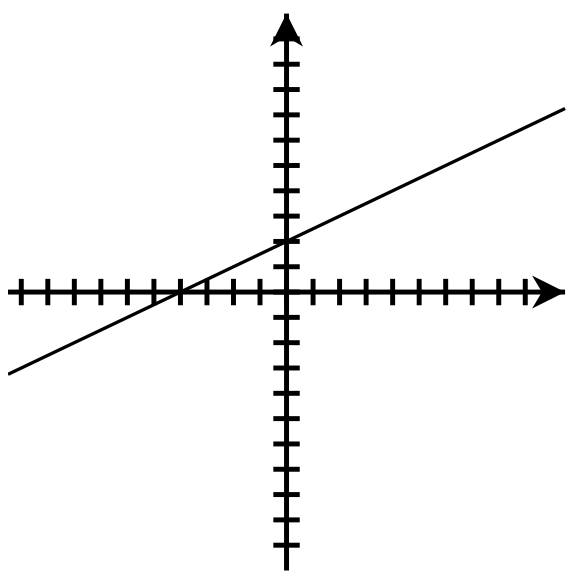
- y-intercept: [latex](0, -1)[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](-8, 0)[/latex]
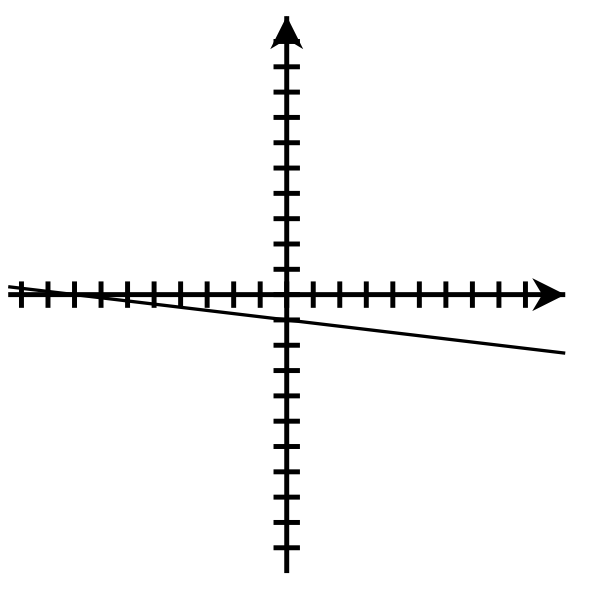
- y-intercept: [latex](0, \frac{1}{3})[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](-3, 0)[/latex]
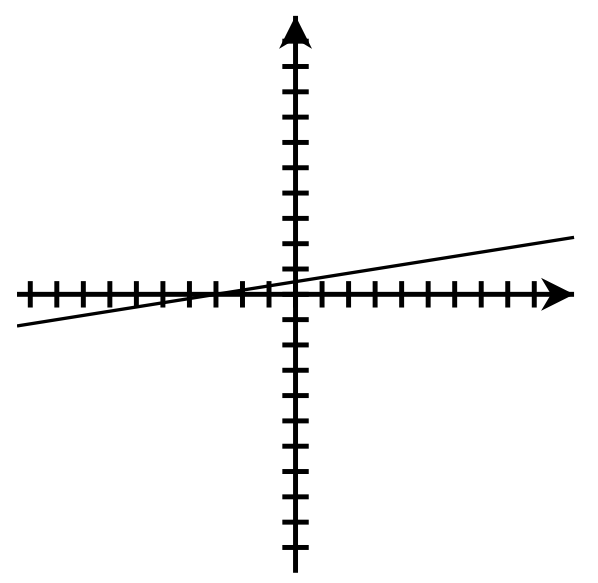
- y-intercept: [latex](0, 4)[/latex]; x-intercept: none
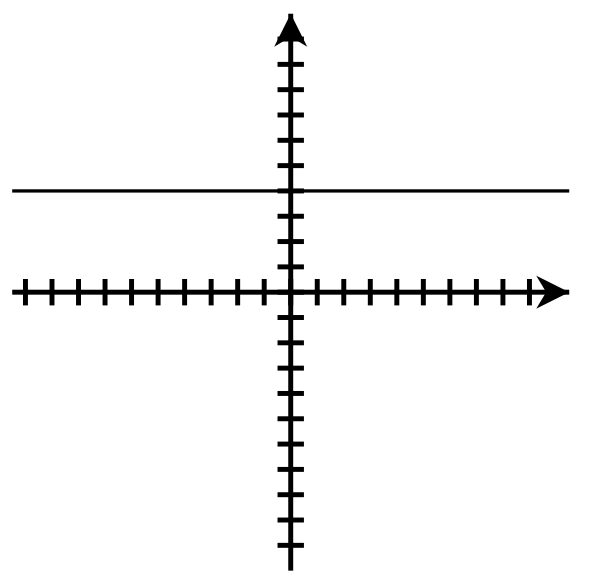
- y-intercept: none; x-intercept: [latex](-2, 0)[/latex]
Homework: Intercepts Method
- Answers may vary.
- Answers may vary.
- y-intercept: [latex](0, 8)[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](\frac{8}{3}, 0)[/latex]
- y-intercept: [latex](0, -2)[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](6, 0)[/latex]
- y-intercept: [latex](0, \frac{2}{3})[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](-\frac{1}{2}, 0)[/latex]
- y-intercept: [latex](0, -3)[/latex]; x-intercept: none
- y-intercept: [latex](0, -2)[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](6, 0)[/latex]
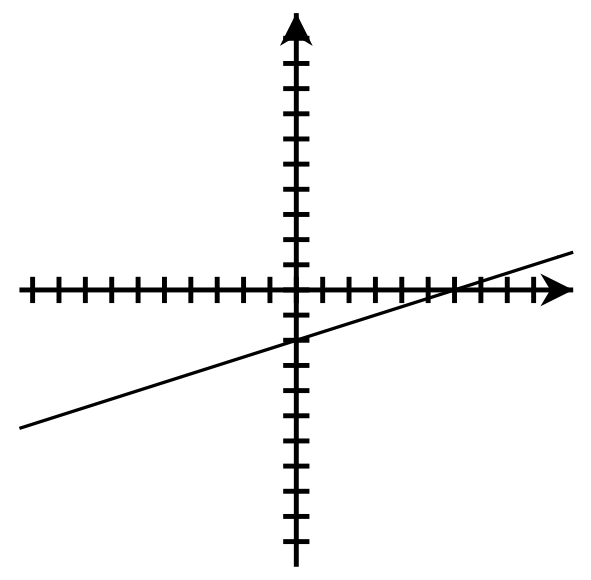
- y-intercept: [latex](0, -1)[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](3, 0)[/latex]
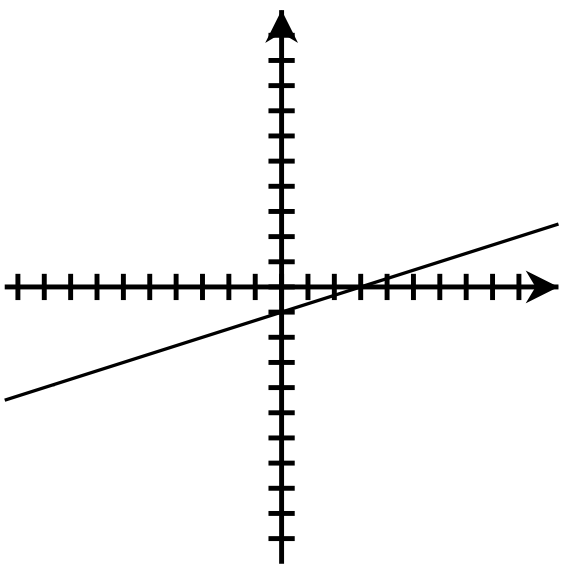
- y-intercept: [latex](0, 3)[/latex]; x-intercept: [latex](9, 0)[/latex]
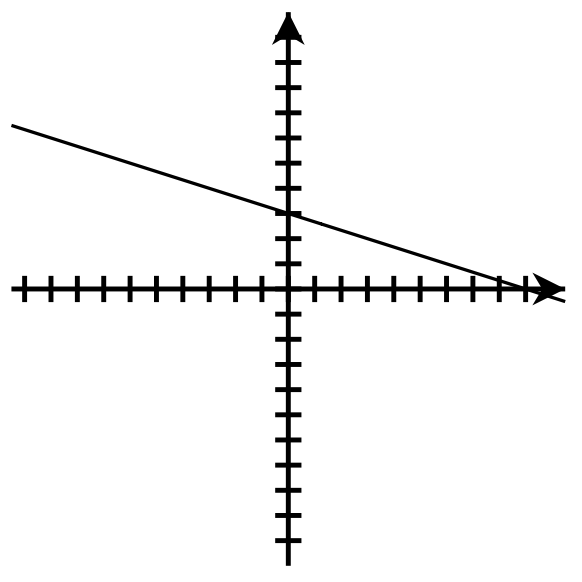
- y-intercept: none; x-intercept: [latex](4, 0)[/latex]
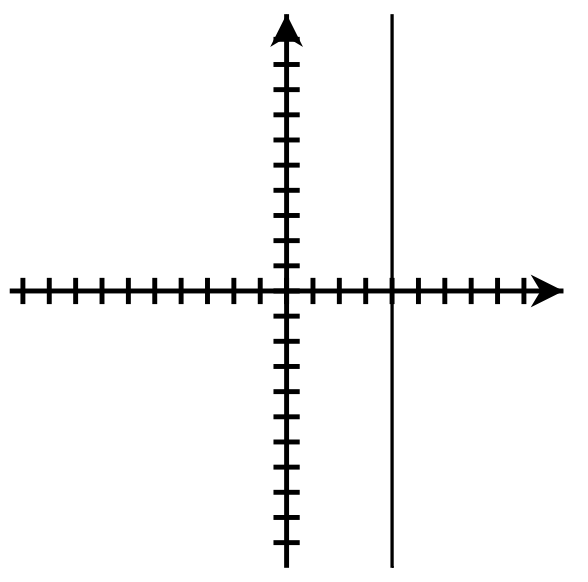
- Answers may vary.
- Discuss with a classmate.
-
- [latex](0,-6)[/latex]
- [latex](0,-6)[/latex]
- Explain.
- Explain.
- Explain.
Prep: Linear Graphs - Slope-Intercept Method
- [latex]y = \frac{3}{2}x + 4[/latex]
- [latex]y = -x + 3[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\frac{2}{3}x + 5[/latex]
- [latex]y = x - 3[/latex]
- [latex]y = -2x - 1[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\frac{1}{3}x - 1[/latex]
- [latex]y = 2x - 6[/latex]
- [latex]y = \frac{3}{4}x - 6[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\frac{1}{4}x + 3[/latex]
- [latex]y = -x - 6[/latex]
- [latex]y = \frac{1}{6}x - \frac{1}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\frac{2}{3}x + 4[/latex]
- [latex]3[/latex]
- [latex]-\frac12[/latex]
- [latex]-\frac{12}7[/latex]
- [latex]-\frac{29}{28}[/latex]
- [latex]0[/latex]
- Undefined
- Discuss with classmates.
Classwork: Slope-Intercept Method
- [latex]y = \frac{3}{2}x + 4[/latex];
[latex]m = \frac{3}{2}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, 4)[/latex] - [latex]y = -x + 3[/latex];
[latex]m = -1[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, 3)[/latex] - [latex]y = -\frac{2}{3}x + 5[/latex];
[latex]m = -\frac{2}{3}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, 5)[/latex] - [latex]y = 2x - 3[/latex];
[latex]m = 2[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -3)[/latex] - [latex]y = -4[/latex];
[latex]m = 0[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -4)[/latex] - [latex]x = 16[/latex];
m is undefined; y-intercept: none - [latex]y = \frac{1}{6}x - \frac{1}{3}[/latex];
[latex]m = \frac{1}{6}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -\frac{1}{3})[/latex] - [latex]y = \frac{3}{4}x - 6[/latex];
[latex]m = \frac{3}{4}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -6)[/latex] - Answers may vary.
- Many answers possible.
- [latex]y = -\frac{2}{3}x + 5[/latex];
[latex]m = -\frac{2}{3}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, 5)[/latex]
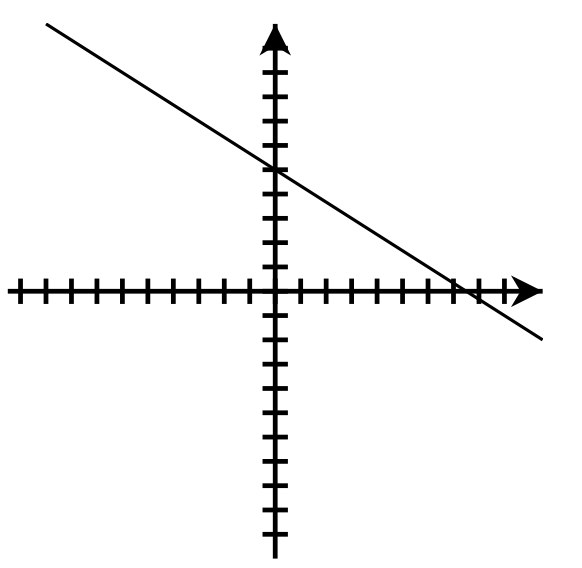
- [latex]y = 5x + 1[/latex];
[latex]m = 5[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, 1)[/latex]
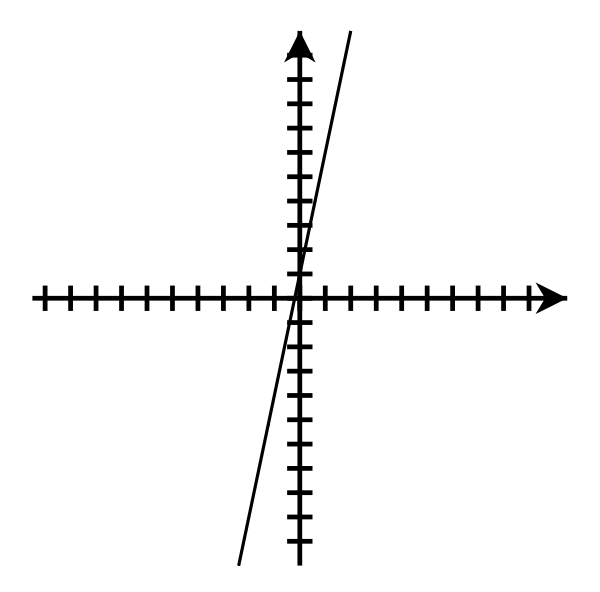
- [latex]y = \frac{5}{2}x - 2[/latex];
[latex]m = \frac{5}{2}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -2)[/latex]
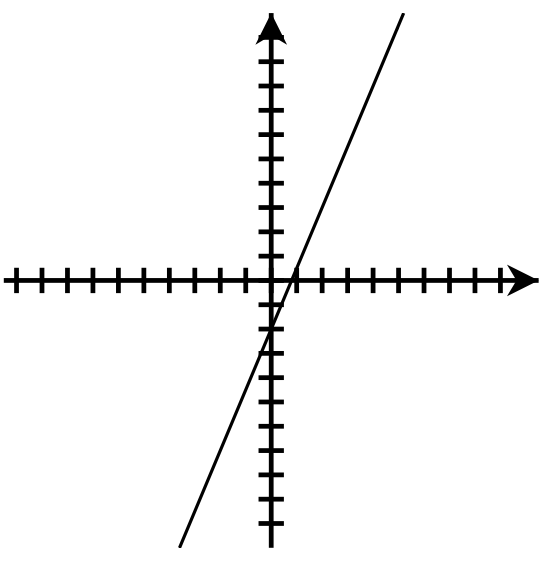
- [latex]y = \frac{1}{2}x - \frac{4}{3}[/latex];
[latex]m = \frac{1}{2}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -\frac{4}{3})[/latex]
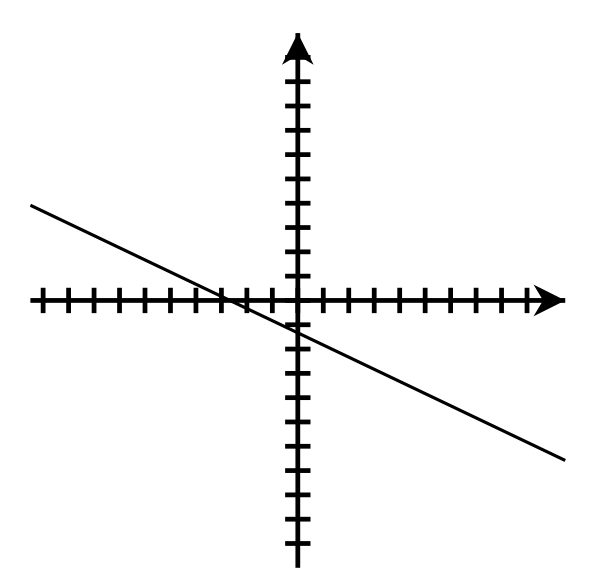
- [latex]y = 4x[/latex];
x-intercept: [latex](0, 0)[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, 0)[/latex]. Use the slope to find another point.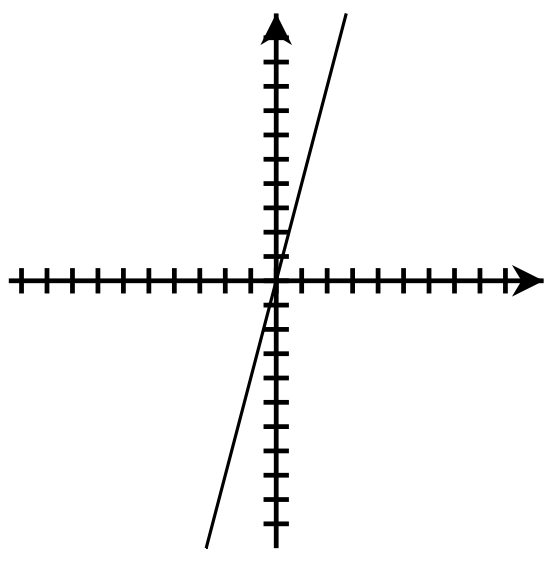
- Compare your answers with your classmates.
- [latex]m = -\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]m = -2[/latex]
- [latex]m = -\frac{3}{8}[/latex]
- [latex]m = \frac{96}{35}[/latex]
- [latex]m = 0[/latex]
- m is undefined
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
-
- [latex]m = -\frac{2}{5}[/latex]
- [latex]m = -\frac{2}{5}[/latex]
- The slopes are equal;
their graphs are parallel.
-
- [latex]m = \frac{1}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]m = -3[/latex]
- The slopes are negative reciprocals;
their graphs are perpendicular.
Homework: Slope-Intercept Method
- [latex]y = -\frac{12}{25}x + 12[/latex];
[latex]m = -\frac{12}{25}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, 12)[/latex] - [latex]y = \frac{1}{3}x - 3[/latex];
[latex]m = \frac{1}{3}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -3)[/latex] - [latex]y = -x + 4[/latex];
[latex]m = -1[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, 4)[/latex] - [latex]y = -\frac{1}{4}x - \frac{2}{3}[/latex];
[latex]m = -\frac{1}{4}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -\frac{2}{3})[/latex] - [latex]y = \frac{3}{4}x - \frac{15}{2}[/latex];
[latex]m = \frac{3}{4}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -\frac{15}{2})[/latex] - [latex]y = -3[/latex];
[latex]m = 0[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -3)[/latex]
- Answers may vary.
- Explain.
- [latex]m = -\frac{3}{2}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -5)[/latex]
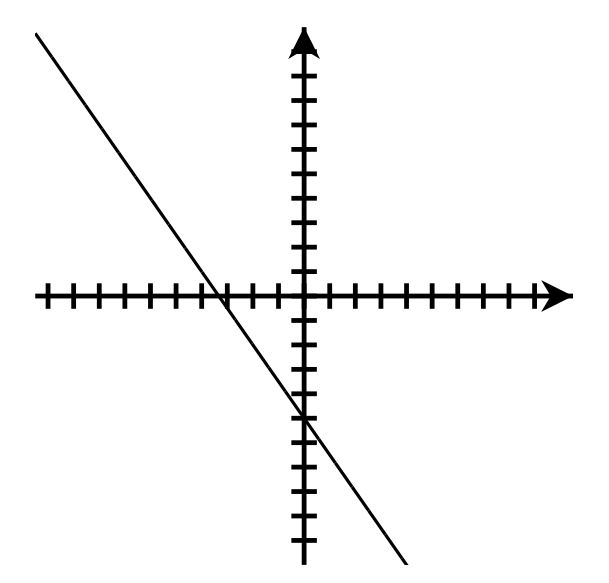
- [latex]y = -\frac{1}{3}x + 3[/latex];
[latex]m = -\frac{1}{3}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, 3)[/latex]
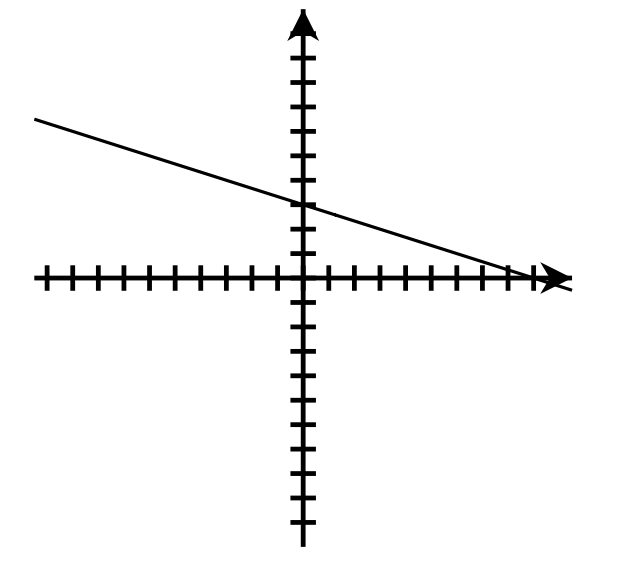
- [latex]y = \frac{1}{4}x - 3[/latex];
[latex]m = \frac{1}{4}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -3)[/latex]
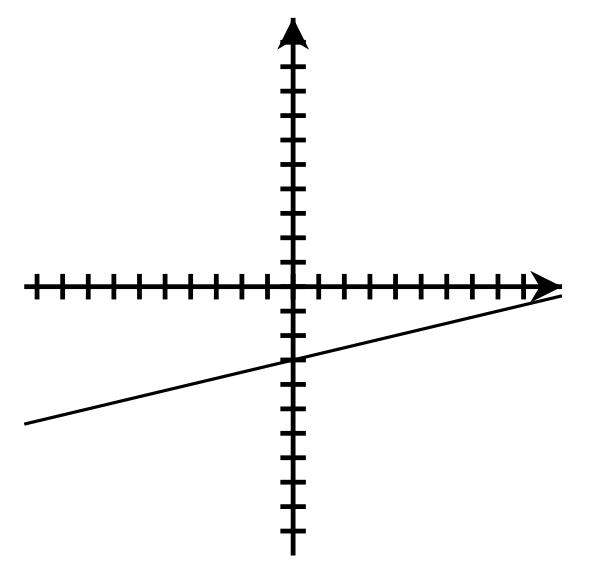
- [latex]y = 2x + 3[/latex];
[latex]m = 2[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, 3)[/latex]
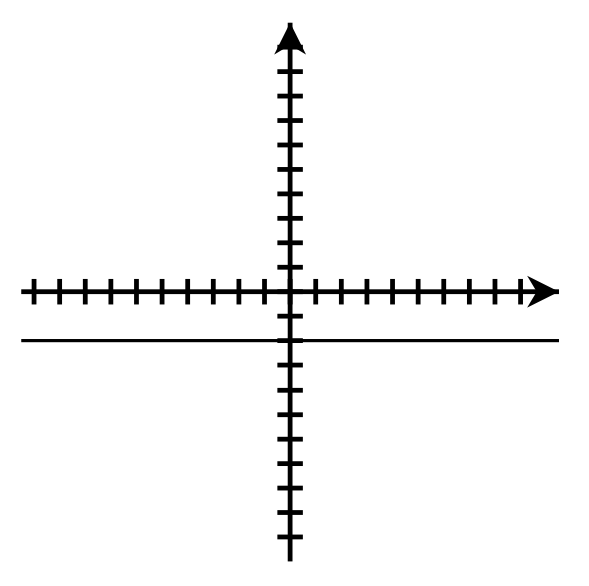
- [latex]y = -2[/latex];
[latex]m = 0[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -2)[/latex]
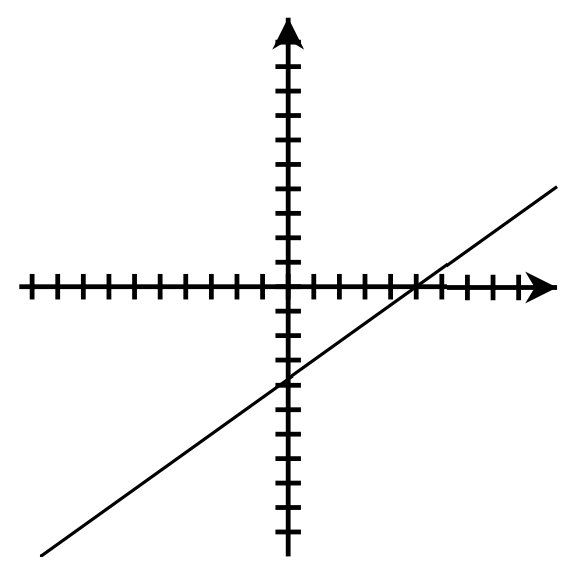
- [latex]y = \frac{3}{4}x - \frac{15}{4}[/latex];
[latex]m = \frac{3}{4}[/latex]; y-intercept: [latex](0, -\frac{15}{4})[/latex]
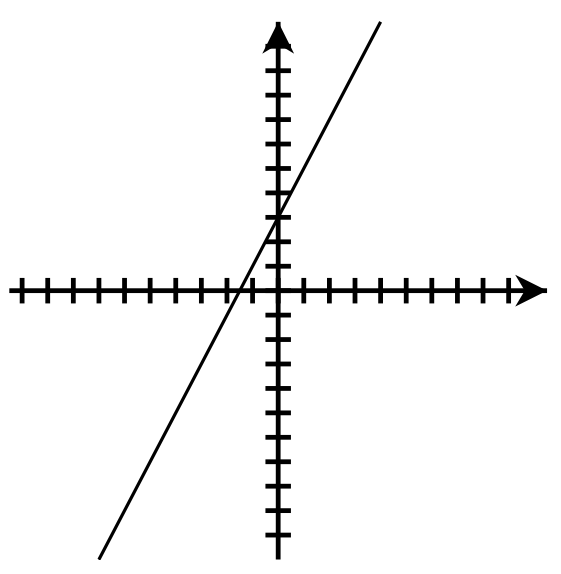
- [latex]m = -\frac{1}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]m = 1[/latex]
- [latex]m = -\frac{11}{9}[/latex]
- [latex]m = -\frac{12}{35}[/latex]
- [latex]m = -\frac{81}{170}[/latex]
- (A) and (C) are parallel; Both (A) and (C) are perpendicular to (B)
Prep: Function Notation and Applications of Linear Functions
- [latex]-6[/latex]
- [latex]14[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{7}{10}[/latex]
- [latex]-\frac{13}{16}[/latex]
- [latex]-17[/latex]
- [latex]147.75[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{3}{4}[/latex]
- [latex]t = 14[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{13}{30}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{3}{2}[/latex]
- Independent: Time (months)
Dependent: Weight (lb)
Rate: 4 lbs per month - Independent: Sales ($)
Dependent: Salary ($)
Rate: Not given - Independent: Credit hours
Dependent: Cost ($)
Rate: $80 per hour - Independent: Number of visits
Dependent: Cost ($)
Rate: $4.50 per visit - Independent: Altitude
Dependent: Temperature
Rate: Not given - Independent: Time (years)
Dependent: Meals out
Rate: Not given
Classwork: Function Notation & Linear Applications
- [latex]-32[/latex], input, [latex](-3, -32)[/latex]
- [latex]-5[/latex], input, [latex](0, -5)[/latex]
- [latex]10[/latex], output, [latex](10, 85)[/latex]
- [latex]9a - 5[/latex], input
- [latex]1[/latex], input, [latex](\frac{2}{3}, 1)[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{5}{9}[/latex], output, [latex](\frac{5}{9}, 0)[/latex]
- [latex]4[/latex]
- [latex]1[/latex]
- [latex]4[/latex]
- [latex]0[/latex]
- [latex]-6[/latex]
- [latex]-1[/latex]
- [latex]-3[/latex]
- [latex]-4[/latex]
- $37.50
- Answers will vary by current year.
-
- 260 pounds
- 4 pounds per month
- 15.5 months
- The y-intercept is [latex](0, 20000)[/latex] which means her salary is $20,000 at $0 in sales.
The slope is [latex]m = 0.3[/latex], which means her salary increases by $0.30 per $1.00 in sales. -
- Explain
- Check with your neighbor
- 128 visits
-
- The temperature decreases by 3.5°F per thousand ft. gain in elevation.
- 16.6°F
- 7,600 feet
- 251 meals in 2030
- Many answers are possible.
- Because the rate of change is not constant
- 3 liters of 1% low-fat; 1.8% fat in the mixture
Homework: Function Notation & Linear Applications
- [latex]-5[/latex], input, [latex](-3, -5)[/latex]
- [latex]23[/latex], input, [latex](4, 23)[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{13}{2}[/latex], output, [latex](\frac{13}{2}, 33)[/latex]
- [latex]31[/latex], input, [latex](6, 31)[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{15}{2}[/latex], input, [latex](\frac{1}{8}, \frac{15}{2})[/latex]
- [latex]-\frac{7}{4}[/latex], output, [latex](-\frac{7}{4}, 0)[/latex]
- Explain
- Discuss.
- [latex]f(-2) = 0[/latex]
- [latex]f(1) = -1.5[/latex]
- [latex]f(4) = 6[/latex]
- [latex]f(0) = -6[/latex]
- [latex]x = -1.9, 0.6[/latex]
- [latex]x = -2.1, 3.4[/latex]
- [latex]x = -1[/latex]
- [latex]x = -2, 2, 3[/latex]
- 66 beats
- Answers will vary by current year.
-
- [latex]C(x) = 115x + 1000[/latex]
- [latex]C(12) = $2,380[/latex]
-
- $99 is the initial cost
- DVR costs $5.99 per month
- [latex]C(24) = $242.76[/latex]
-
- Explain
- Check with a classmate
- 29 miles
-
- $200
- $3.00
- 200 desserts
-
- [latex]m = -88.2[/latex];
Credit card debt decreases by $88.20 per year - [latex]D(x) = -88.2x + 7768[/latex]
- $5563
- [latex]m = -88.2[/latex];
- 14 gallons of 1% acid; 21 gallons of 2%

