Quadratic Functions
Prep for Graphing Quadratic Functions
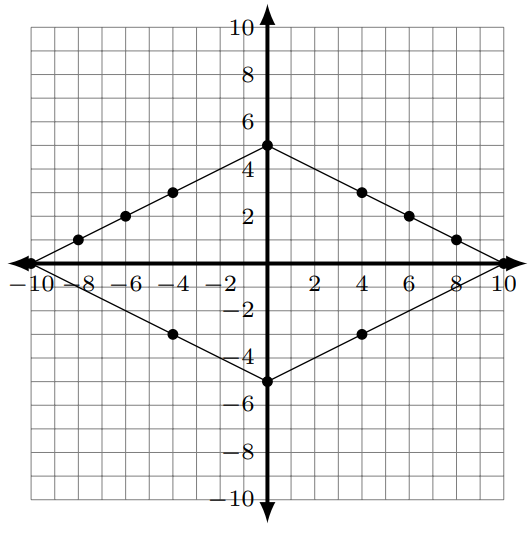
- [latex]\begin{array}{lc}B&\left(0,1\right)\\F&1\\C\;or\;D\;\;&x=1\\C\;or\;D&x=1\\A&\left(1,0\right)\\E&y=1\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]y=3[/latex]
- [latex]x=3[/latex]
- [latex](-3,0)[/latex]
- Explain
- [latex]-4[/latex]
- [latex]-\frac32[/latex]
- [latex]4[/latex]
-
- [latex]-\frac56[/latex]
- [latex]\frac12[/latex]
- [latex]-10[/latex]
-
- [latex]57[/latex]
- [latex]5[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{19}2[/latex]
-
- [latex]-26[/latex]
- [latex]-2[/latex]
- [latex]4[/latex]
-
- [latex]-13[/latex]
- [latex]-\frac{89}{16}[/latex]
- [latex]-\frac{41}4[/latex]
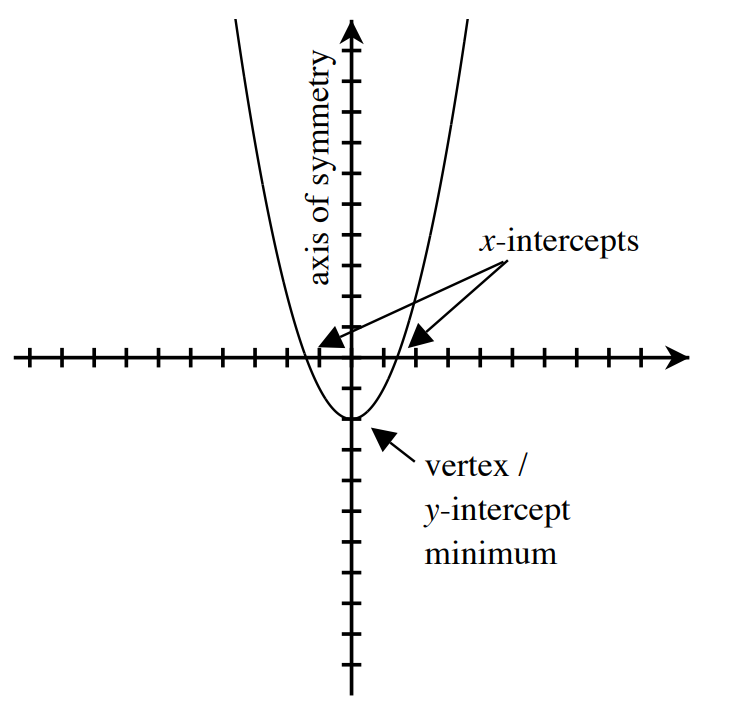
- An intercept is a point where a graph touches the x- or y-axis.
-
- y-intercept: (0, 2); x-intercept: (-5, 0)
- y-intercept: (0, -2); x-intercepts: (-2, 0), (1, 0)
-
- Yes
- No
- Infinity and negative infinity; Discuss with classmates.
Classwork: Graphing Quadratic Functions
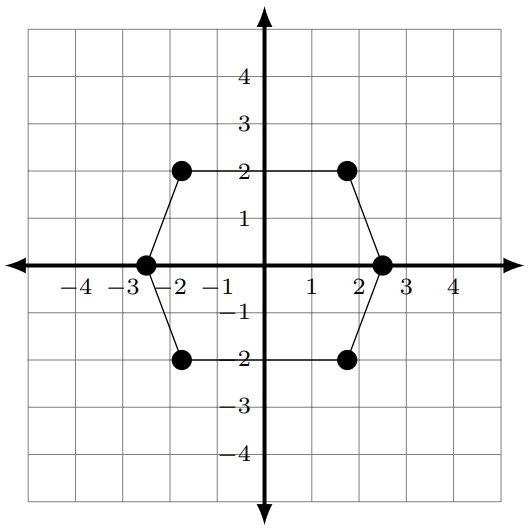
- 2
- none
- 1
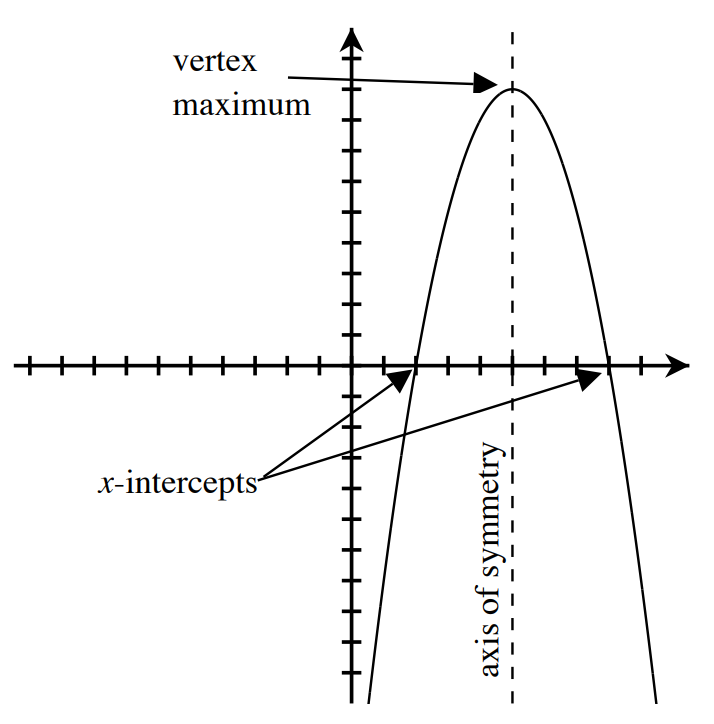
Graph A
- [latex]x=3[/latex]
- [latex](3,4)[/latex]
- maximum
- Domain [latex]=\left(-\infty,\infty\right);[/latex] Range [latex]=(-\infty,4\rbrack[/latex]
- [latex](0,-5)[/latex]
- The points are symmetric across the axis of symmetry.
Graph B
- [latex]x=-2[/latex]
- [latex](-2,-5)[/latex]
- maximum
- D [latex]=\left(-\infty,\infty\right);[/latex] R [latex]=\lbrack-5,\infty)[/latex]
- [latex](0,-1)[/latex]
- The points are symmetric across the axis of symmetry.
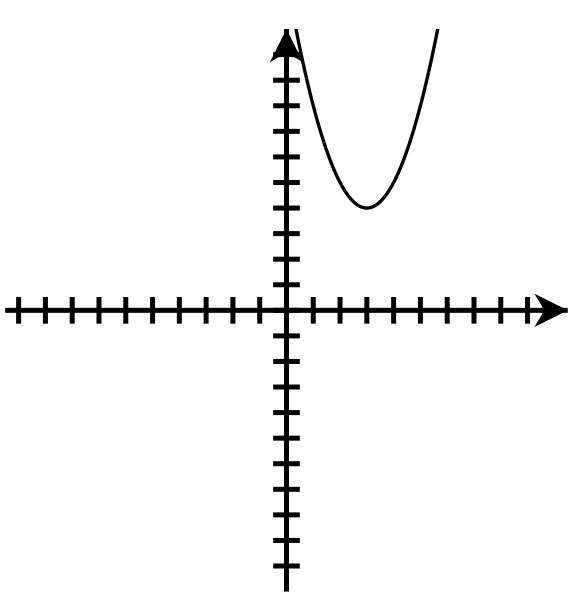
Up
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=3[/latex]
Vertex: [latex](3,4)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,13)[/latex]
Number of x-intercepts: none
Domain : [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex]\lbrack4,\infty)[/latex]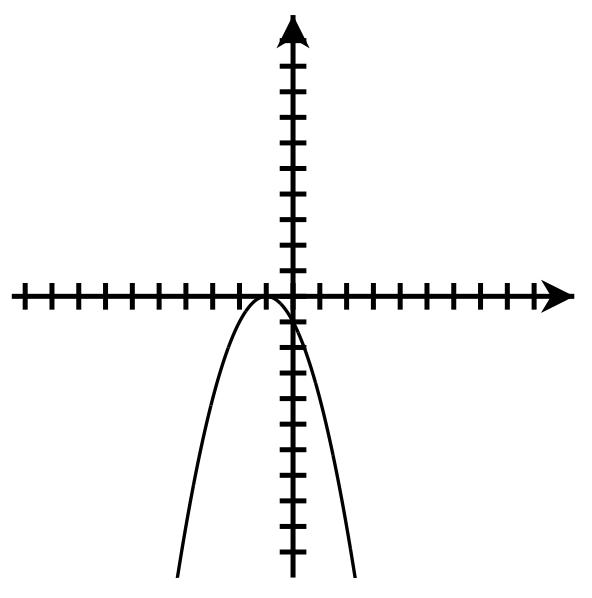
Down
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=-1[/latex]
Vertex: [latex](-1,0)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,-1)[/latex]
Number of x-intercepts: 1
Domain : [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex](-\infty,0\rbrack[/latex]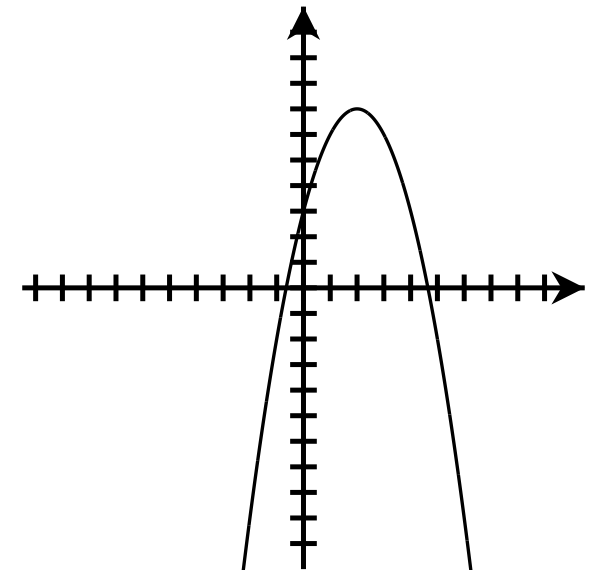
Down
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=2[/latex]
Vertex: [latex](2,7)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,3)[/latex]
Number of x-intercepts: 2
Domain : [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex](-\infty,7\rbrack[/latex]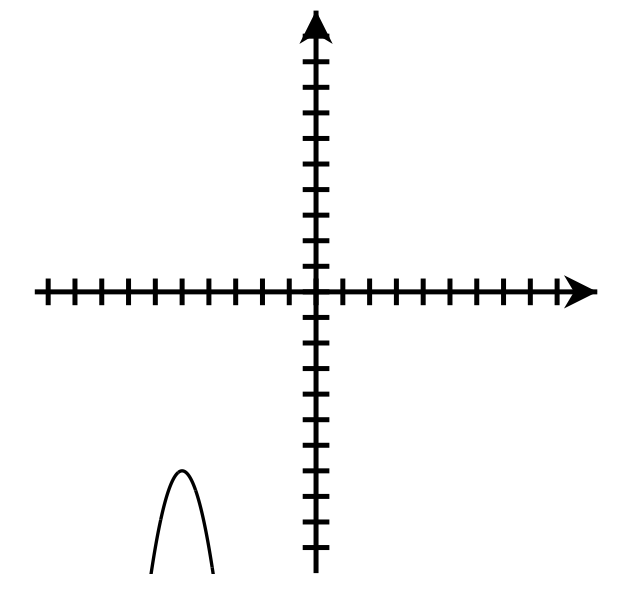
Down
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=-5[/latex]
Vertex: [latex](-5,-7)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,-82)[/latex]
Number of x-intercepts: none
Domain : [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex](-\infty,-7\rbrack[/latex]
Homework: Graphing Quadratic Functions
- Explain.
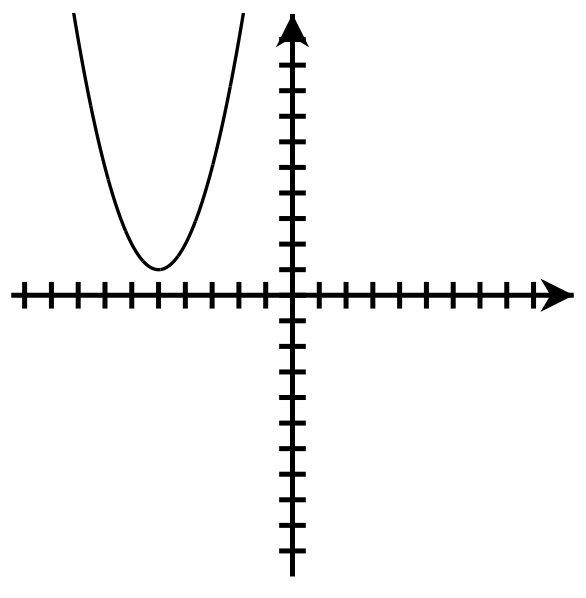
Up
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=-5[/latex]
Vertex: [latex](-5,1)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,26)[/latex]
Number of x-intercepts: none
Domain : [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex]\lbrack1,\infty)[/latex]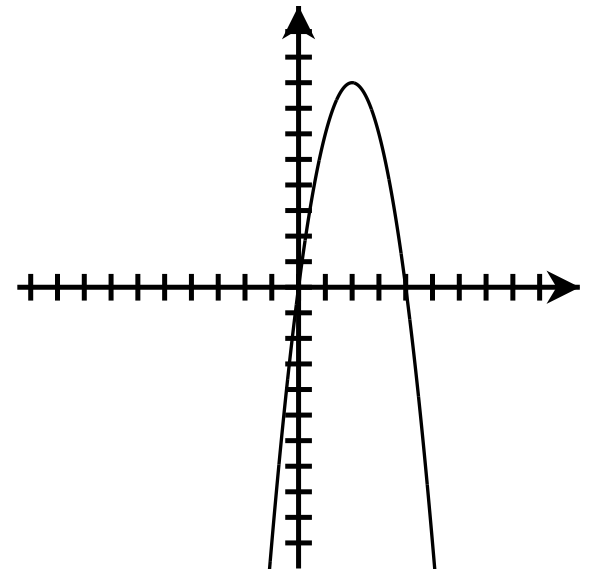
Down
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=2[/latex]
Vertex: [latex](2,8)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,0)[/latex]
Number of x-intercepts: 2
Domain : [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex](-\infty,8\rbrack[/latex]
Explain.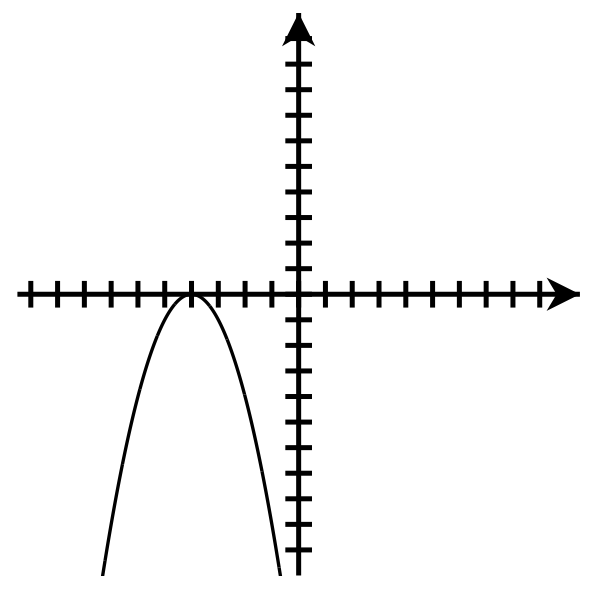
Down
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=-4[/latex]
Vertex: [latex](-4,0)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,-16)[/latex]
Number of x-intercepts: 1
Domain : [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex](-\infty,0\rbrack[/latex]
Explain.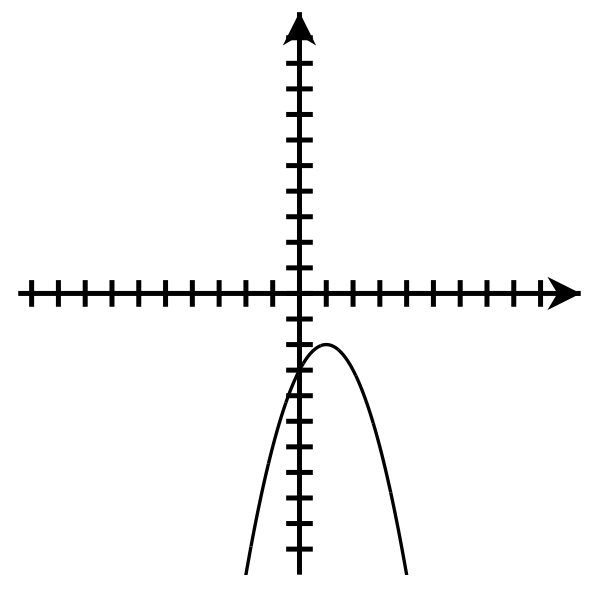
Down
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=-1[/latex]
Vertex: [latex](1,-2)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,-3)[/latex]
Number of x-intercepts: none
Domain : [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex](-\infty,-2\rbrack[/latex]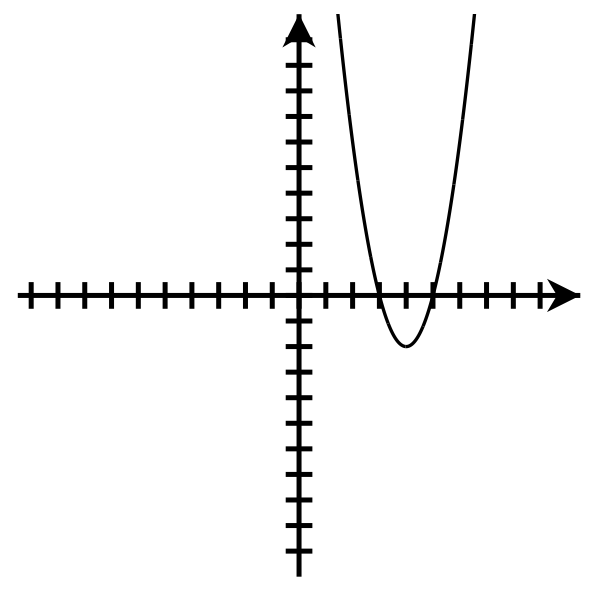
Up
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=-4[/latex]
Vertex: [latex](4,-2)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,30)[/latex]
Number of x-intercepts: 2
Domain : [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex]\lbrack-2,\infty)[/latex]- Answers may vary.
Prep for Applications of Quadratic Functions
-
- meters per second
- 58.8 m
- [latex]D\left(t\right)=-4.9t^2+19.6t+58.8[/latex]
- The distance from the ground in meters
- When does the object strike the ground?
-
- feet per second
- height above the ground
- feet
- time
- seconds
- the graph is a parabola opening down.
-
- seconds
- meters
- seconds
-
- feet
- seconds
- Discuss
- exact
- approximate
- exact
- approximate
- exact
- approximate
- [latex]=[/latex]
- [latex]\approx[/latex]
- [latex]\approx[/latex]
- [latex]=[/latex]
- [latex]\approx[/latex]
- [latex]\approx[/latex]
- [latex]\approx[/latex]
- [latex]=[/latex]
- [latex]\approx[/latex]
- [latex]3,600[/latex]
- [latex]45[/latex]
- [latex]39.82[/latex]
- [latex]72.49[/latex]
- [latex]-3.094[/latex]
- [latex]0.3[/latex]
- [latex]0.3[/latex]
- [latex]0.59[/latex]
Classwork: Applications of Quadratic Functions
-
- 8 sec
- 256 ft
-
- 192 ft
- Up
-
- 192 ft
- Down
- 1 second, 7 seconds
- from 0 to 1 because it covered more distance.
- Domain [latex]=\left[0,8\right][/latex]; Range [latex]=\left[0,256\right][/latex]
-
- [latex](0,0)[/latex]
- Discuss
- Discuss
- x-intercept is used for domain; vertex is used for range
-
-
x y 0 23 3 311 6 311 9 23 10 −137 - 23 ft
- 311 ft
- 347 ft
- between 9 and 10 secs
-
-
- 2 meters
- [latex]2.30625[/latex] meters
- The ball is never above 3 meters
- The skateboarder is about 0.86 ft above the ground at the bottom of the half-pipe. The bottom of the half-pipe is 6.75 ft away from the starting point of the ride.
-
- 25 feet
- 25 feet at [latex]t=0[/latex]
-
- No, the maximum height is [latex]12.25[/latex] feet.
- 6 feet
Homework: Applications of Quadratic Functions
-
-
x y 0 80 1 124 2 136 3 116 4 64 5 −20 - 80 ft
- 134 ft
- 136.25 ft
- between 4 and 5 seconds
-
-
- 8 feet
- 0.625 seconds
- 14.25 feet
-
- [latex](0, 0)[/latex]
- Discuss
- Discuss
- x-intercept is used for domain; vertex is used for range
- Answers may vary
-
- 33 feet
- 0.375 seconds
- 35.25 feet
-
- There are 4,540 parking spaces at 7 A.M.
- There are only 40 parking spaces at 10 A.M.
- The maximum height is 52 meters at time [latex]t=0[/latex]
Prep for Solving Using Quadratic Formula
- 5
- 10
- [latex]\sqrt{889}[/latex]
- Discuss with a classmate
- [latex]2\sqrt{3}[/latex]
- [latex]6\sqrt{2}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{7 \pm \sqrt{3}}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]-1, 7[/latex]
- [latex]1 \pm \sqrt{5}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{5\pm\sqrt5}2[/latex]
- [latex]6i[/latex]
- [latex]6i\sqrt{2}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{2}{5}i[/latex]
- [latex]-3 \pm \frac{3}{2}i[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{5}{2} \pm \frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}i[/latex]
- [latex]2 \pm 3i[/latex]
Classwork: Solving Using the Quadratic Formula
- [latex]x = 2 \pm \sqrt{7}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm i\sqrt{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{-5 \pm \sqrt{33}}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{3}{2} \pm \frac{\sqrt{11}}{2}i[/latex]
- [latex]x = -3[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{3 \pm \sqrt{13}}{4}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{3 \pm \sqrt{29}}{10}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{7}{2} \pm \frac{\sqrt{23}}{2}i[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \frac{5}{2}i[/latex]
- [latex]x = 4, -\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{-1 \pm \sqrt{11}}{4}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{9}{2}, 0[/latex]
- 2
- 1
- none
- Discuss.
- Check with your classmate.
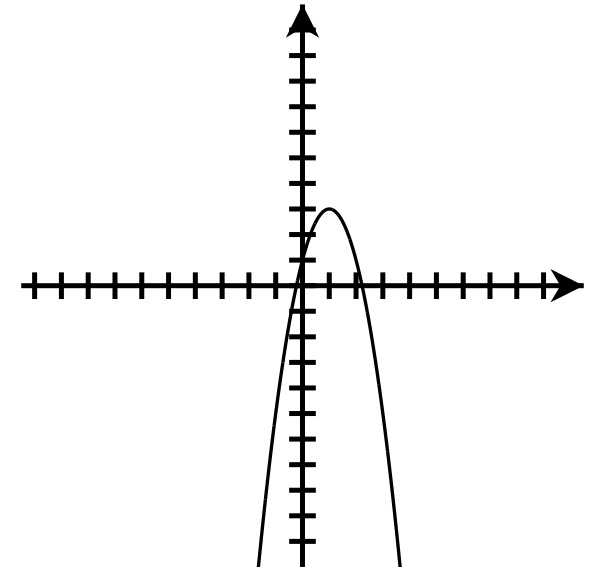
- Down
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=1[/latex]
Vertex: (1,3)
y-intercept: (0,1)
x-intercepts: [latex]\left(\frac{2\pm\sqrt6}2,0\right)[/latex]
Domain: [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex](-\infty,3\rbrack[/latex]
-
- 293 feet
- 329 feet
- 2 seconds, 7 seconds
- 9.03 seconds
- Domain [latex]=[0,9.03][/latex]; Range [latex]=[0,329][/latex]
- The will hit the ground in approximately 2.33 sec
Homework: Solving Using the Quadratic Formula
- [latex]5\sqrt{7}[/latex]
- [latex]3 \pm \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]10i\sqrt{3}[/latex]
- [latex]5 \pm \frac{i\sqrt{30}}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{7}{2}, -\frac{5}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{17}{20}, -\frac{10}{29}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{5 \pm \sqrt{109}}{6}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \frac{\sqrt{2}}{4}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 4 \pm \sqrt{6}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{3}{4} \pm \frac{\sqrt{51}}{4}i[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{1}{3} \pm \frac{\sqrt{71}}{3}i[/latex]
- [latex]x = 1[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{5 \pm \sqrt{17}}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 0, 2[/latex]
- Explain.
- Discuss.
- Check with a classmate.
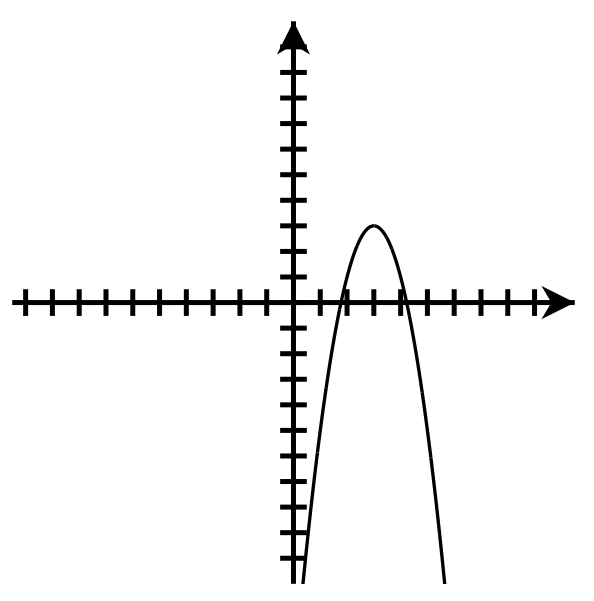
- Down
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=3[/latex]
Vertex: (3,3)
y-intercept: (0,-15)
x-intercepts: [latex]\left(\frac{6\pm\sqrt6}2,0\right);[/latex]
Domain: [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex](-\infty,3\rbrack[/latex]
- 1.57 seconds
- 1.45 seconds
- [latex]\approx10.32[/latex] seconds longer
-
- 2 seconds
- 382 feet
- Domain [latex]=[0,4.763][/latex]; Range [latex]=[0,382][/latex]
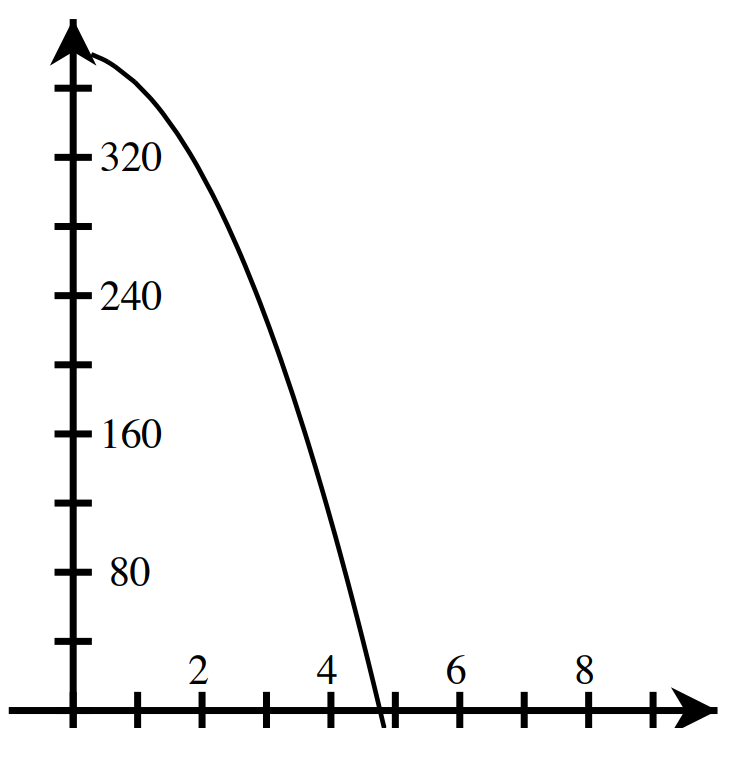
Classwork: Solving Using the Square Root Method
- [latex]x = \pm 4[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm 10[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm 5i[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm 9i[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm i\sqrt{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm i[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \sqrt{15}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \frac{3\sqrt{11}}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm 4[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \frac{2\sqrt{2}}{7}i[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm 2\sqrt{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \sqrt{41}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \sqrt{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \sqrt{23}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm 8[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \frac{2}{3}i[/latex]
- 1.25 seconds
- [latex]x=\pm\frac{\sqrt5}3[/latex]
- Explain.
- Discuss.
Homework: Solving Using the Square Root Method
- Many answers possible.
- [latex]x = \pm 7[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \sqrt{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm 2i[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \frac{9}{2}i[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm \sqrt{46}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \pm 2\sqrt{7}[/latex]
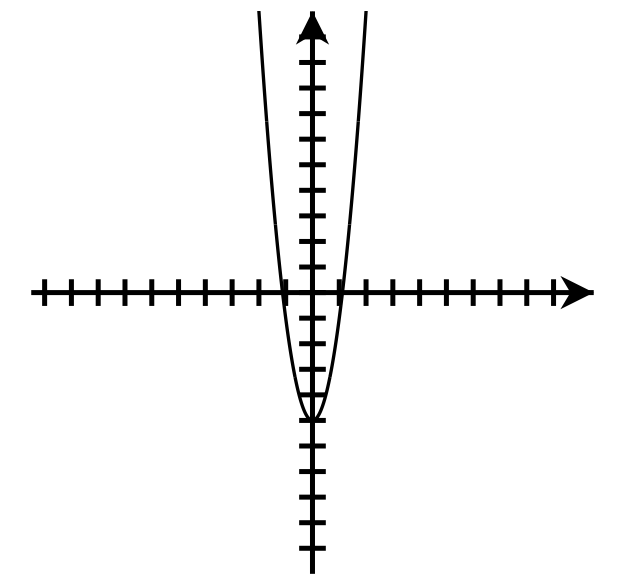
- Up
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=0[/latex]
Vertex:[latex](0,-5)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,-5)[/latex]
x-intercepts: [latex]\left(\pm\frac{\sqrt5}2,0\right)[/latex]
Domain:[latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex]\lbrack-5,\infty)[/latex]
- 3.26 seconds
- Answers may vary
- Many answers possible.
Prep for Solving Equations by Factoring
- [latex]10(y^2 + 1)[/latex]
- [latex]3t(t + 2)[/latex]
- [latex]3x^2(5 - 7x^3)[/latex]
- [latex]6x^4(4 + 5x^3)[/latex]
- [latex]6(x^2 - 4x + 5)[/latex]
- [latex]2x(4x^2 + 6x - 5)[/latex]
- [latex](5x + 2y)(3z + 4)[/latex]
- [latex](6x^2 + 5)(4x - 7)[/latex]
- [latex]3x(x - 1)(y - 2)[/latex]
- [latex](3x - 2)(3y + 10x)[/latex]
- [latex]2(4x - 5)(7x + 3y)[/latex]
- [latex](4x - 5)(2y + 3)[/latex]
- [latex](x - 2)(x - 4)[/latex]
- [latex](x + 1)(x - 15)[/latex]
- [latex](x - 4)(x + 7)[/latex]
- [latex](x - 3)^2[/latex]
- [latex](x + 5)(x - 2)[/latex]
- [latex](x - 5)(x + 3)[/latex]
- [latex]7(x - 5)(x - 1)[/latex]
- [latex]3(x + 4)(x - 2)[/latex]
- [latex](2x - 1)(3x + 2)[/latex]
- [latex](5x - 4)(x - 2)[/latex]
- [latex](3x - 2)(x + 5)[/latex]
- Prime
- [latex](4x - 3)(2x + 3)[/latex]
- [latex](5x + 7)(2x + 1)[/latex]
- [latex](x - 2)(3x + 1)[/latex]
- [latex](3x - 2)(4x + 3)[/latex]
- [latex](x + 7)(x - 7)[/latex]
- [latex](2x + 9)(2x - 9)[/latex]
- Prime
- [latex]2x(4x + 1)(4x - 1)[/latex]
- [latex]25(x^2 + 4)[/latex]
- [latex](7 - x)(7 + x)[/latex]
- [latex]x(x + 1)(x - 1)[/latex]
- [latex]3x(x + 2)(x - 2)[/latex]
Classwork: Solving Equations by Factoring
- [latex]x = \frac{4}{3}, -\frac{4}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -7, -1[/latex]
- [latex]x = -3, -\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 3[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{5}{2}, 0[/latex]
- [latex]t = -3, -6[/latex]
- [latex]x = 0, \frac{1}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -2, \frac{3}{4}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{1}{5}, -\frac{8}{5}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -2, 2[/latex]
- [latex]x = 8, -8[/latex]
- [latex]t = \frac{7}{4}, -\frac{7}{4}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 2, \frac{3}{4}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{5}{3}, -\frac{6}{5}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 5, -\frac{7}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]t = \frac{3}{2}, -\frac{8}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{3}{2}, \frac{25}{6}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{2}{5}, \frac{1}{3}, 0[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{7}{3}, \frac{4}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 0, -\frac{3}{4}, \frac{3}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]t = -\frac{1}{3}, \frac{2}{5}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{3}{4}, \frac{2}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 3, \frac{2}{7}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -4, -\frac{1}{6}[/latex]
- [latex]x=-\frac49,\frac49[/latex]
- [latex]x = 2, -2[/latex]
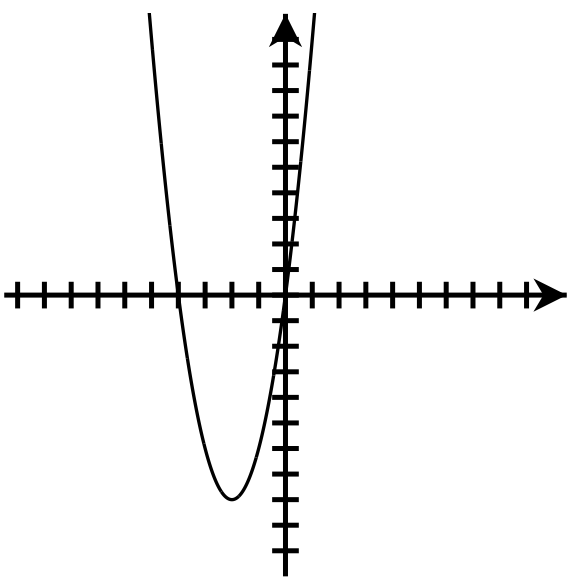
- Up
Axis of symmetry:[latex]x=-2[/latex]
Vertex:[latex](-2,-8)[/latex]
y-intercept:[latex](0, 0)[/latex]
x-intercepts:[latex](0, 0),(-4, 0)[/latex]
Domain: [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex]\lbrack-8,\infty)[/latex]
-
- 8 second, 7 seconds
- 1
- [latex]x=0,-3[/latex]
- Explain.
Homework: Solving Equations by Factoring
- [latex]x = -3, -5[/latex]
- [latex]t = \pm \frac{5}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{5}{3}, -\frac{3}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 0, -10[/latex]
- [latex]t = -\frac{3}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 6, -\frac{1}{4}[/latex]
- [latex]x = \frac{4}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{4}{3}, 3[/latex]
- [latex]x = 0, -6, 2[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{2}{3}, -\frac{4}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 0, \frac{1}{5}[/latex]
- [latex]t = -3, -\frac{3}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]t = 4, \frac{3}{5}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 0, \pm \frac{3}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -6, \frac{1}{4}, 0[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{5}{2}, 1[/latex]
- [latex]x = 0, \frac{1}{4}[/latex]
- [latex]x = 5, -5[/latex]
- [latex]t = \frac{4}{5}, -\frac{2}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]x = -\frac{5}{2}, \frac{3}{4}[/latex]
- Answers may vary.
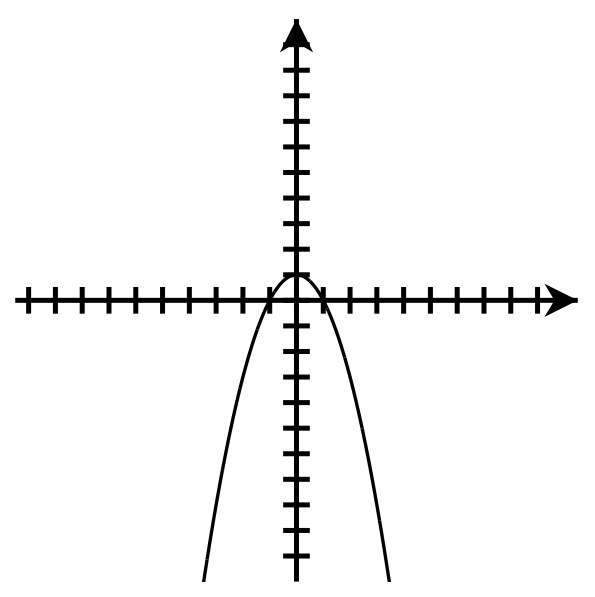
- Down
Axis of symmetry: [latex]x=0[/latex]
Vertex: [latex](0,1)[/latex]
y-intercept: [latex](0,1)[/latex]
x-intercepts: [latex](-1,0),(1,0)[/latex]
Domain: [latex]\left(-\infty,\infty\right)[/latex]
Range: [latex](-\infty,1\rbrack[/latex]
-
- 1 seconds, 3 seconds
- 5 seconds
- Answers may vary.
- Explain.