Chapter 4: States of Consciousness
4.2 Sleep and Dreaming
Learning Objectives
- Describe areas of the brain and hormone secretions involved in sleep
- Describe several theories (adaptive and cognitive) aimed at explaining the function of sleep
- Differentiate between REM and non-REM sleep
- Describe the stages of sleep
- Describe and differentiate between theories on why we dream
- Describe the symptoms and treatments for insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy
Introduction to Sleep and Dreams
What you’ll learn to do: describe what happens to the brain and body during sleep
We devote a very large portion of time to sleep, and our brains have complex systems that control various aspects of sleep. Several hormones important for physical growth and maturation are secreted during sleep. While the reason we sleep remains something of a mystery, there is some evidence to suggest that sleep is very important to learning and memory.
You may not feel particularly busy while you sleep, but you’ll learn in this section that your brain and body are quite active. You pass through four different stages of sleep. In this section, you’ll learn more about these sleep stages, dreaming, and sleep disorders.
Sleep and Why We Sleep
We spend approximately one-third of our lives sleeping. Given the average life expectancy for U.S. citizens falls between 73 and 79 years old (Singh & Siahpush, 2006), we can expect to spend approximately 25 years of our lives sleeping. Some animals never sleep (e.g., several fish and amphibian species); other animals can go extended periods of time without sleep and without apparent negative consequences (e.g., dolphins); yet some animals (e.g., rats) die after two weeks of sleep deprivation (Siegel, 2008). Why do we devote so much time to sleeping? Is it absolutely essential that we sleep? This section will consider these questions and explore various explanations for why we sleep.
What is Sleep?
You have read that sleep is distinguished by low levels of physical activity and reduced sensory awareness. As discussed by Siegel (2008), a definition of sleep must also include mention of the interplay of the circadian and homeostatic mechanisms that regulate sleep. Homeostatic regulation of sleep is evidenced by sleep rebound following sleep deprivation. Sleep rebound refers to the fact that a sleep-deprived individual will tend to take longer falling asleep during subsequent opportunities for sleep. Sleep is characterized by certain patterns of activity of the brain that can be visualized using electroencephalography (EEG), and different phases of sleep can be differentiated using EEG as well (Figure 1).
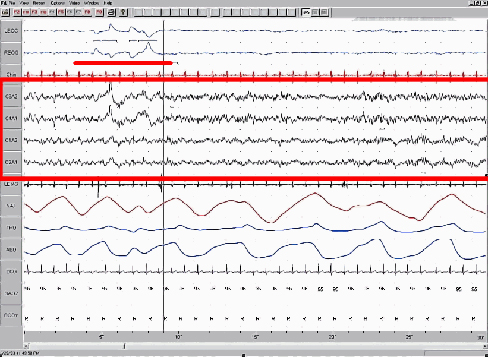
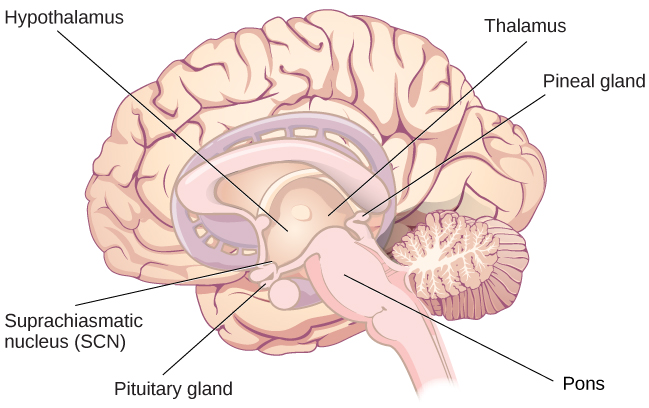
Sleep-wake cycles seem to be controlled by multiple brain areas acting in conjunction with one another. Some of these areas include the thalamus, the hypothalamus, and the pons. As already mentioned, the hypothalamus contains the SCN—the biological clock of the body—in addition to other nuclei that, in conjunction with the thalamus, regulate slow-wave sleep. The pons is important for regulating rapid eye movement (REM) sleep (National Institutes of Health, n.d.).
Sleep is also associated with the secretion and regulation of a number of hormones from several endocrine glands including: melatonin, follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and growth hormone (National Institutes of Health, n.d.). You have read that the pineal gland releases melatonin during sleep (Figure 2). Melatonin is thought to be involved in the regulation of various biological rhythms and the immune system (Hardeland et al., 2006). During sleep, the pituitary gland secretes both FSH and LH which are important in regulating the reproductive system (Christensen et al., 2012; Sofikitis et al., 2008). The pituitary gland also secretes growth hormone, during sleep, which plays a role in physical growth and maturation as well as other metabolic processes (Bartke, Sun, & Longo, 2013).
Why Do We Sleep?
Given the central role that sleep plays in our lives and the number of adverse consequences that have been associated with sleep deprivation, one would think that we would have a clear understanding of why it is that we sleep. Unfortunately, this is not the case; however, several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the function of sleep.
Adaptive Function of Sleep
One popular hypothesis of sleep incorporates the perspective of evolutionary psychology. Evolutionary psychology is a discipline that studies how universal patterns of behavior and cognitive processes have evolved over time as a result of natural selection. Variations and adaptations in cognition and behavior make individuals more or less successful in reproducing and passing their genes to their offspring. One hypothesis from this perspective might argue that sleep is essential to restore resources that are expended during the day. Just as bears hibernate in the winter when resources are scarce, perhaps people sleep at night to reduce their energy expenditures. While this is an intuitive explanation of sleep, there is little research that supports this explanation. In fact, it has been suggested that there is no reason to think that energetic demands could not be addressed with periods of rest and inactivity (Frank, 2006; Rial et al., 2007), and some research has actually found a negative correlation between energetic demands and the amount of time spent sleeping (Capellini, Barton, McNamara, Preston, & Nunn, 2008).
Another evolutionary hypothesis of sleep holds that our sleep patterns evolved as an adaptive response to predatory risks, which increase in darkness. Thus we sleep in safe areas to reduce the chance of harm. Again, this is an intuitive and appealing explanation for why we sleep. Perhaps our ancestors spent extended periods of time asleep to reduce attention to themselves from potential predators. Comparative research indicates, however, that the relationship that exists between predatory risk and sleep is very complex and equivocal. Some research suggests that species that face higher predatory risks sleep fewer hours than other species (Capellini et al., 2008), while other researchers suggest there is no relationship between the amount of time a given species spends in deep sleep and its predation risk (Lesku, Roth, Amlaner, & Lima, 2006).
It is quite possible that sleep serves no single universally adaptive function, and different species have evolved different patterns of sleep in response to their unique evolutionary pressures. While we have discussed the negative outcomes associated with sleep deprivation, it should be pointed out that there are many benefits that are associated with adequate amounts of sleep. A few such benefits listed by the National Sleep Foundation (n.d.) include maintaining healthy weight, lowering stress levels, improving mood, and increasing motor coordination, as well as a number of benefits related to cognition and memory formation.
Cognitive Function of Sleep
Another theory regarding why we sleep involves sleep’s importance for cognitive function and memory formation (Rattenborg, Lesku, Martinez-Gonzalez, & Lima, 2007). Indeed, we know sleep deprivation results in disruptions in cognition and memory deficits (Brown, 2012), leading to impairments in our abilities to maintain attention, make decisions, and recall long-term memories. Moreover, these impairments become more severe as the amount of sleep deprivation increases (Alhola & Polo-Kantola, 2007). Furthermore, slow-wave sleep after learning a new task can improve resultant performance on that task (Huber, Ghilardi, Massimini, & Tononi, 2004) and seems essential for effective memory formation (Stickgold, 2005). Understanding the impact of sleep on cognitive function should help you understand that cramming all night for a test may be not effective and can even prove counterproductive.
Watch It
Watch this video to learn more about the function of sleep and the harmful effects of sleep deprivation.
Sleep has also been associated with other cognitive benefits. Research indicates that included among these possible benefits are increased capacities for creative thinking (Cai, Mednick, Harrison, Kanady, & Mednick, 2009; Wagner, Gais, Haider, Verleger, & Born, 2004), language learning (Fenn, Nusbaum, & Margoliash, 2003; Gómez, Bootzin, & Nadel, 2006), and inferential judgments (Ellenbogen, Hu, Payne, Titone, & Walker, 2007). It is possible that even the processing of emotional information is influenced by certain aspects of sleep (Walker, 2009).
Watch It
Learn about the connection between memory and sleep in the following clip:
Try It
Think It Over
Have you (or someone you know) ever experienced significant periods of sleep deprivation because of simple insomnia, high levels of stress, or as a side effect from a medication? What were the consequences of missing out on sleep?
Stages of Sleep
Sleep is not a uniform state of being. Instead, sleep is composed of several different stages that can be differentiated from one another by the patterns of brain wave activity that occur during each stage. These changes in brain wave activity can be visualized using EEG and are distinguished from one another by both the frequency and amplitude of brain waves. Sleep can be divided into two different general phases: REM sleep and non-REM (NREM) sleep. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep is characterized by darting movements of the eyes under closed eyelids. Brain waves during REM sleep appear very similar to brain waves during wakefulness. In contrast, non-REM (NREM) sleep is subdivided into three stages distinguished from each other and from wakefulness by characteristic patterns of brain waves. The first three stages of sleep are NREM sleep, while the fourth and final stage of sleep is REM sleep. In this section, we will discuss each of these stages of sleep and their associated patterns of brain wave activity.
[Note that psychologists originally identified four stages of non-REM sleep, but these were revised in 2008, resulting in just three distinct phases of NREM sleep. You will see that stage 3 of NREM sleep is sometimes presented as both stage 3 and stage 4 in various texts.]
NREM Stages of Sleep
The first stage of NREM sleep is known as stage 1 sleep. Stage 1 sleep is a transitional phase that occurs between wakefulness and sleep, the period during which we drift off to sleep. During this time, there is a slowdown in both the rates of respiration and heartbeat. In addition, stage 1 sleep involves a marked decrease in both overall muscle tension and core body temperature.
In terms of brain wave activity, stage 1 sleep is associated with both alpha and theta waves. The early portion of stage 1 sleep produces alpha waves, which are relatively low frequency (8–13Hz), high amplitude patterns of electrical activity (waves) that become synchronized. This pattern of brain wave activity resembles that of someone who is very relaxed, yet awake. As an individual continues through stage 1 sleep, there is an increase in theta wave activity. Theta waves are even lower frequency (4–7 Hz), higher amplitude brain waves than alpha waves. It is relatively easy to wake someone from stage 1 sleep; in fact, people often report that they have not been asleep if they are awoken during stage 1 sleep.

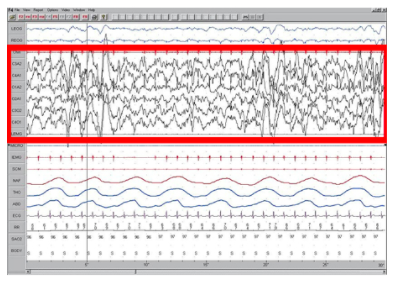
As we move into stage 2 sleep, the body goes into a state of deep relaxation. Theta waves still dominate the activity of the brain, but they are interrupted by brief bursts of activity known as sleep spindles (Figure 3). A sleep spindle is a rapid burst of higher frequency brain waves that may be important for learning and memory (Fogel & Smith, 2011; Poe, Walsh, & Bjorness, 2010). In addition, the appearance of K-complexes is often associated with stage 2 sleep. A K-complex is a very high amplitude pattern of brain activity that may in some cases occur in response to environmental stimuli. Thus, K-complexes might serve as a bridge to higher levels of arousal in response to what is going on in our environments (Halász, 1993; Steriade & Amzica, 1998).

Stage 3 of sleep is often referred to as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep because these stages are characterized by low frequency (up to 4 Hz), high amplitude delta waves (Figure 4). During this time, an individual’s heart rate and respiration slow dramatically. It is much more difficult to awaken someone from sleep during stage 3 than during earlier stages. Interestingly, individuals who have increased levels of alpha brain wave activity (more often associated with wakefulness and transition into stage 1 sleep) during stage 3 often report that they do not feel refreshed upon waking, regardless of how long they slept (Stone, Taylor, McCrae, Kalsekar, & Lichstein, 2008).
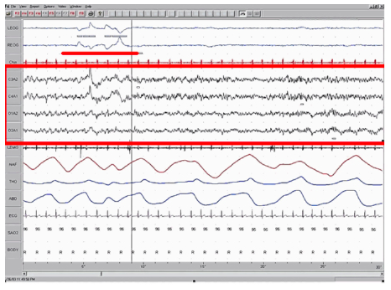
REM Sleep
As mentioned earlier, REM sleep is marked by rapid movements of the eyes. The brain waves associated with this stage of sleep are very similar to those observed when a person is awake, as shown in Figure 5, and this is the period of sleep in which dreaming occurs. It is also associated with paralysis of muscle systems in the body with the exception of those that make circulation and respiration possible. Therefore, no movement of voluntary muscles occurs during REM sleep in a normal individual; REM sleep is often referred to as paradoxical sleep because of this combination of high brain activity and lack of muscle tone. Like NREM sleep, REM has been implicated in various aspects of learning and memory (Wagner, Gais, & Born, 2001), although there is disagreement within the scientific community about how important both NREM and REM sleep are for normal learning and memory (Siegel, 2001).
If people are deprived of REM sleep and then allowed to sleep without disturbance, they will spend more time in REM sleep in what would appear to be an effort to recoup the lost time in REM. This is known as the REM rebound, and it suggests that REM sleep is also homeostatically regulated. Aside from the role that REM sleep may play in processes related to learning and memory, REM sleep may also be involved in emotional processing and regulation. In such instances, REM rebound may actually represent an adaptive response to stress in nondepressed individuals by suppressing the emotional salience of aversive events that occurred in wakefulness (Suchecki, Tiba, & Machado, 2012).
While sleep deprivation in general is associated with a number of negative consequences (Brown, 2012), the consequences of REM deprivation appear to be less profound (as discussed in Siegel, 2001). In fact, some have suggested that REM deprivation can actually be beneficial in some circumstances. For instance, REM sleep deprivation has been demonstrated to improve symptoms of people suffering from major depression, and many effective antidepressant medications suppress REM sleep (Riemann, Berger, & Volderholzer, 2001; Vogel, 1975).
It should be pointed out that some reviews of the literature challenge this finding, suggesting that sleep deprivation that is not limited to REM sleep is just as effective or more effective at alleviating depressive symptoms among some patients suffering from depression. In either case, why sleep deprivation improves the mood of some patients is not entirely understood (Giedke & Schwärzler, 2002). Recently, however, some have suggested that sleep deprivation might change emotional processing so that various stimuli are more likely to be perceived as positive in nature (Gujar, Yoo, Hu, & Walker, 2011). The hypnogram below (Figure 6) shows a person’s passage through the stages of sleep.

Think It Over
Researchers believe that one important function of sleep is to facilitate learning and memory. How does knowing this help you in your college studies? What changes could you make to your study and sleep habits to maximize your mastery of the material covered in class?
Dreams and Dreaming
Dreams
The meaning of dreams varies across different cultures and periods of time. By the late 19th century, German psychiatrist Sigmund Freud had become convinced that dreams represented an opportunity to gain access to the unconscious. By analyzing dreams, Freud thought people could increase self-awareness and gain valuable insight to help them deal with the problems they faced in their lives. Freud made distinctions between the manifest content and the latent content of dreams.
Manifest content is the actual content, or storyline, of a dream. Latent content, on the other hand, refers to the hidden meaning of a dream. For instance, if a woman dreams about being chased by a snake, Freud might have argued that this represents the woman’s fear of sexual intimacy, with the snake serving as a symbol of a man’s penis.
Freud was not the only theorist to focus on the content of dreams. The 20th century Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung believed that dreams allowed us to tap into the collective unconscious. The collective unconscious, as described by Jung, is a theoretical repository of information he believed to be shared by everyone. According to Jung, certain symbols in dreams reflected universal archetypes with meanings that are similar for all people regardless of culture or location.
The sleep and dreaming researcher Rosalind Cartwright, however, believes that dreams simply reflect life events that are important to the dreamer. Unlike Freud and Jung, Cartwright’s ideas about dreaming have found empirical support. For example, she and her colleagues published a study in which women going through divorce were asked several times over a five month period to report the degree to which their former spouses were on their minds. These same women were awakened during REM sleep in order to provide a detailed account of their dream content. There was a significant positive correlation between the degree to which women thought about their former spouses during waking hours and the number of times their former spouses appeared as characters in their dreams (Cartwright, Agargun, Kirkby, & Friedman, 2006). Recent research (Horikawa, Tamaki, Miyawaki, & Kamitani, 2013) has uncovered new techniques by which researchers may effectively detect and classify the visual images that occur during dreaming by using fMRI for neural measurement of brain activity patterns, opening the way for additional research in this area.

Recently, neuroscientists have also become interested in understanding why we dream. For example, Hobson (2009) suggests that dreaming may represent a state of protoconsciousness. In other words, dreaming involves constructing a virtual reality in our heads that we might use to help us during wakefulness. Among a variety of neurobiological evidence, John Hobson cites research on lucid dreams as an opportunity to better understand dreaming in general. Lucid dreams are dreams in which certain aspects of wakefulness are maintained during a dream state. In a lucid dream, a person becomes aware of the fact that they are dreaming, and as such, they can control the dream’s content (LaBerge, 1990).
Theories on Dreaming
While the Freudian theory of dreaming may be the most well known, and Cartwright’s suggestions on dreaming the most plausible, there are several other theories about the purpose of dreaming. The threat-simulation theory suggests that dreaming should be seen as an ancient biological defense mechanism. Dreams are thought to provide an evolutionary advantage because of their capacity to repeatedly simulate potential threatening events. This process enhances the neurocognitive mechanisms required for efficient threat perception and avoidance.
The expectation-fulfillment theory posits that dreaming serves to discharge emotional arousals (however minor) that haven’t been expressed during the day. This practice frees up space in the brain to deal with the emotional arousals of the next day and allows instinctive urges to stay intact. In effect, the expectation is fulfilled (the action is “completed”) in a metaphorical form so that a false memory is not created. This theory explains why dreams are usually forgotten immediately afterwards.
One prominent neurobiological theory of dreaming is the activation-synthesis theory, which states that dreams don’t actually mean anything. They are merely electrical brain impulses that pull random thoughts and imagery from our memories. The theory posits that humans construct dream stories after they wake up, in a natural attempt to make sense of the nonsensical. However, given the vast documentation of the realistic aspects of human dreaming, as well as indirect experimental evidence that other mammals such as cats also dream, evolutionary psychologists have theorized that dreaming does indeed serve a purpose.
The continual-activation theory proposes that dreaming is a result of brain activation and synthesis. Dreaming and REM sleep are simultaneously controlled by different brain mechanisms. The hypothesis states that the function of sleep is to process, encode, and transfer data from short-term memory to long-term memory through a process called consolidation. However, there is not much evidence to back this up. NREM sleep processes the conscious-related memory (declarative memory), and REM sleep processes the unconscious related memory (procedural memory).
The underlying assumption of continual-activation theory is that, during REM sleep, the unconscious part of the brain is busy processing procedural memory. Meanwhile, the level of activation in the conscious part of the brain descends to a very low level as the inputs from the senses are basically disconnected. This triggers the “continual-activation” mechanism to generate a data stream from the memory stores to flow through to the conscious part of the brain.
Link to Learning
Review the purpose and stages of sleep as well as the reasons why we dream in the following CrashCourse video:
Sleep Problems and Disorders
Many people experience disturbances in their sleep at some point in their lives. Depending on the population and sleep disorder being studied, between 30% and 50% of the population suffers from a sleep disorder at some point in their lives (Bixler, Kales, Soldatos, Kaels, & Healey, 1979; Hossain & Shapiro, 2002; Ohayon, 1997, 2002; Ohayon & Roth, 2002). This section will describe several sleep disorders as well as some of their treatment options.
Parasomnias
A parasomnia is one of a group of sleep disorders in which unwanted, disruptive motor activity and/or experiences during sleep play a role. Parasomnias can occur in either REM or NREM phases of sleep. Sleepwalking, restless leg syndrome, and night terrors are all examples of parasomnias (Mahowald & Schenck, 2000).
Sleepwalking
In sleepwalking, or somnambulism, the sleeper engages in relatively complex behaviors ranging from wandering about to driving an automobile. During periods of sleepwalking, sleepers often have their eyes open, but they are not responsive to attempts to communicate with them. Sleepwalking most often occurs during slow-wave sleep, but it can occur at any time during a sleep period in some affected individuals (Mahowald & Schenck, 2000).
Historically, somnambulism has been treated with a variety of pharmacotherapies ranging from benzodiazepines to antidepressants. However, the success rate of such treatments is questionable. Guilleminault et al. (2005) found that sleepwalking was not alleviated with the use of benzodiazepines. However, all of their somnambulistic patients who also suffered from sleep-related breathing problems showed a marked decrease in sleepwalking when their breathing problems were effectively treated.
Dig Deeper: A Sleepwalking Defense?
On January 16, 1997, Scott Falater sat down to dinner with his wife and children and told them about difficulties he was experiencing on a project at work. After dinner, he prepared some materials to use in leading a church youth group the following morning, and then he attempted repair the family’s swimming pool pump before retiring to bed. The following morning, he awoke to barking dogs and unfamiliar voices from downstairs. As he went to investigate what was going on, he was met by a group of police officers who arrested him for the murder of his wife (Cartwright, 2004; CNN, 1999).
Yarmila Falater’s body was found in the family’s pool with 44 stab wounds. A neighbor called the police after witnessing Falater standing over his wife’s body before dragging her into the pool. Upon a search of the premises, police found blood-stained clothes and a bloody knife in the trunk of Falater’s car, and he had blood stains on his neck.
Remarkably, Falater insisted that he had no recollection of hurting his wife in any way. His children and his wife’s parents all agreed that Falater had an excellent relationship with his wife and they couldn’t think of a reason that would provide any sort of motive to murder her (Cartwright, 2004).
Scott Falater had a history of regular episodes of sleepwalking as a child, and he had even behaved violently toward his sister once when she tried to prevent him from leaving their home in his pajamas during a sleepwalking episode. He suffered from no apparent anatomical brain anomalies or psychological disorders. It appeared that Scott Falater had killed his wife in his sleep, or at least, that is the defense he used when he was tried for his wife’s murder (Cartwright, 2004; CNN, 1999). In Falater’s case, a jury found him guilty of first degree murder in June of 1999 (CNN, 1999); however, there are other murder cases where the sleepwalking defense has been used successfully. As scary as it sounds, many sleep researchers believe that homicidal sleepwalking is possible in individuals suffering from the types of sleep disorders described below (Broughton et al., 1994; Cartwright, 2004; Mahowald, Schenck, & Cramer Bornemann, 2005; Pressman, 2007).
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD)
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) occurs when the muscle paralysis associated with the REM sleep phase does not occur. Individuals who suffer from RBD have high levels of physical activity during REM sleep, especially during disturbing dreams. These behaviors vary widely, but they can include kicking, punching, scratching, yelling, and behaving like an animal that has been frightened or attacked. People who suffer from this disorder can injure themselves or their sleeping partners when engaging in these behaviors. Furthermore, these types of behaviors ultimately disrupt sleep, although affected individuals have no memories that these behaviors have occurred (Arnulf, 2012).
This disorder is associated with a number of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease. In fact, this relationship is so robust that some view the presence of RBD as a potential aid in the diagnosis and treatment of a number of neurodegenerative diseases (Ferini-Strambi, 2011). Clonazepam, an anti-anxiety medication with sedative properties, is most often used to treat RBD. It is administered alone or in conjunction with doses of melatonin (the hormone secreted by the pineal gland). As part of treatment, the sleeping environment is often modified to make it a safer place for those suffering from RBD (Zangini, Calandra-Buonaura, Grimaldi, & Cortelli, 2011).
Other Parasomnias
A person with restless leg syndrome has uncomfortable sensations in the legs during periods of inactivity or when trying to fall asleep. This discomfort is relieved by deliberately moving the legs, which, not surprisingly, contributes to difficulty in falling or staying asleep. Restless leg syndrome is quite common and has been associated with a number of other medical diagnoses, such as chronic kidney disease and diabetes (Mahowald & Schenck, 2000). There are a variety of drugs that treat restless leg syndrome: benzodiazepines, opiates, and anticonvulsants (Restless Legs Syndrome Foundation, n.d.).
Night terrors result in a sense of panic in the sufferer and are often accompanied by screams and attempts to escape from the immediate environment (Mahowald & Schenck, 2000). Although individuals suffering from night terrors appear to be awake, they generally have no memories of the events that occurred, and attempts to console them are ineffective. Typically, individuals suffering from night terrors will fall back asleep again within a short time. Night terrors apparently occur during the NREM phase of sleep (Provini, Tinuper, Bisulli, & Lagaresi, 2011). Generally, treatment for night terrors is unnecessary unless there is some underlying medical or psychological condition that is contributing to the night terrors (Mayo Clinic, n.d.).
Insomnia
While parasomnias are disorders related to the various stages of sleep, other sleep disorders, such as insomnia, are related to sleep in general. Insomnia is a consistent difficulty in falling or staying asleep, and is the most common of the sleep disorders. Individuals with insomnia often experience long delays between the times that they go to bed and actually fall asleep. In addition, these individuals may wake up several times during the night only to find that they have difficulty getting back to sleep. As mentioned earlier, one of the criteria for insomnia involves experiencing these symptoms for at least three nights a week for at least one month’s time (Roth, 2007).
It is not uncommon for people suffering from insomnia to experience increased levels of anxiety about their inability to fall asleep. This becomes a self-perpetuating cycle because increased anxiety leads to increased arousal, and higher levels of arousal make the prospect of falling asleep even more unlikely. Chronic insomnia is almost always associated with feeling overtired and may be associated with symptoms of depression.
There may be many factors that contribute to insomnia, including age, drug use, exercise, mental status, and bedtime routines. Not surprisingly, insomnia treatment may take one of several different approaches. People who suffer from insomnia might limit their use of stimulant drugs (such as caffeine) or increase their amount of physical exercise during the day. Some people might turn to over-the-counter (OTC) or prescribed sleep medications to help them sleep, but this should be done sparingly because many sleep medications result in dependence and alter the nature of the sleep cycle, and they can increase insomnia over time. Those who continue to have insomnia, particularly if it affects their quality of life, should seek professional treatment.
Some forms of psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can help sufferers of insomnia. Cognitive-behavioral therapy is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on cognitive processes and problem behaviors. The treatment of insomnia likely would include stress management techniques and changes in problematic behaviors that could contribute to insomnia (e.g., spending more waking time in bed). Cognitive-behavioral therapy has been demonstrated to be quite effective in treating insomnia (Savard, Simard, Ivers, & Morin, 2005; Williams, Roth, Vatthauer, & McCrae, 2013).
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is defined by episodes during which a sleeper’s breathing stops. These episodes can last 10–20 seconds or longer and often are associated with brief periods of arousal. While individuals suffering from sleep apnea may not be aware of these repeated disruptions in sleep, they do experience increased levels of fatigue. Many individuals diagnosed with sleep apnea first seek treatment because their sleeping partners indicate that they snore loudly and/or stop breathing for extended periods of time while sleeping (Henry & Rosenthal, 2013). Sleep apnea is much more common in overweight people and is often associated with loud snoring. Surprisingly, sleep apnea may exacerbate cardiovascular disease (Sánchez-de-la-Torre, Campos-Rodriguez, & Barbé, 2012). While sleep apnea is less common in thin people, anyone, regardless of their weight, who snores loudly or gasps for air while sleeping, should be checked for sleep apnea.
While people are often unaware of their sleep apnea, they are keenly aware of some of the adverse consequences of insufficient sleep. Consider a patient who believed that as a result of his sleep apnea he “had three car accidents in six weeks. They were ALL my fault. Two of them I didn’t even know I was involved in until afterwards” (Henry & Rosenthal, 2013, p. 52). It is not uncommon for people suffering from undiagnosed or untreated sleep apnea to fear that their careers will be affected by the lack of sleep, illustrated by this statement from another patient, “I’m in a job where there’s a premium on being mentally alert. I was really sleepy… and having trouble concentrating…. It was getting to the point where it was kind of scary” (Henry & Rosenthal, 2013, p. 52).
There are two types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when an individual’s airway becomes blocked during sleep, and air is prevented from entering the lungs. In central sleep apnea, disruption in signals sent from the brain that regulate breathing cause periods of interrupted breathing (White, 2005).
One of the most common treatments for sleep apnea involves the use of a special device during sleep. A continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) device includes a mask that fits over the sleeper’s nose and mouth, which is connected to a pump that pumps air into the person’s airways, forcing them to remain open, as shown in Figure 1. Some newer CPAP masks are smaller and cover only the nose. This treatment option has proven to be effective for people suffering from mild to severe cases of sleep apnea (McDaid et al., 2009). However, alternative treatment options are being explored because consistent compliance by users of CPAP devices is a problem. Recently, a new EPAP (excitatory positive air pressure) device has shown promise in double-blind trials as one such alternative (Berry, Kryger, & Massie, 2011).

SIDS

In sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) an infant stops breathing during sleep and dies. Infants younger than 12 months appear to be at the highest risk for SIDS, and boys have a greater risk than girls. A number of risk factors have been associated with SIDS including premature birth, smoking within the home, and hyperthermia. There may also be differences in both brain structure and function in infants that die from SIDS (Berkowitz, 2012; Mage & Donner, 2006; Thach, 2005).
The substantial amount of research on SIDS has led to a number of recommendations to parents to protect their children (Figure 2). For one, research suggests that infants should be placed on their backs when put down to sleep, and their cribs should not contain any items which pose suffocation threats, such as blankets, pillows or padded crib bumpers (cushions that cover the bars of a crib). Infants should not have caps placed on their heads when put down to sleep in order to prevent overheating, and people in the child’s household should abstain from smoking in the home. Recommendations like these have helped to decrease the number of infant deaths from SIDS in recent years (Mitchell, 2009; Task Force on Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, 2011).
Narcolepsy
Unlike the other sleep disorders described in this section, a person with narcolepsy cannot resist falling asleep at inopportune times. These sleep episodes are often associated with cataplexy, which is a lack of muscle tone or muscle weakness, and in some cases involves complete paralysis of the voluntary muscles. This is similar to the kind of paralysis experienced by healthy individuals during REM sleep (Burgess & Scammell, 2012; Hishikawa & Shimizu, 1995; Luppi et al., 2011). Narcoleptic episodes take on other features of REM sleep. For example, around one third of individuals diagnosed with narcolepsy experience vivid, dream-like hallucinations during narcoleptic attacks (Chokroverty, 2010).
Surprisingly, narcoleptic episodes are often triggered by states of heightened arousal or stress. The typical episode can last from a minute or two to half an hour. Once awakened from a narcoleptic attack, people report that they feel refreshed (Chokroverty, 2010). Obviously, regular narcoleptic episodes could interfere with the ability to perform one’s job or complete schoolwork, and in some situations, narcolepsy can result in significant harm and injury (e.g., driving a car or operating machinery or other potentially dangerous equipment).
Generally, narcolepsy is treated using psychomotor stimulant drugs, such as amphetamines (Mignot, 2012). These drugs promote increased levels of neural activity. Narcolepsy is associated with reduced levels of the signaling molecule hypocretin in some areas of the brain (De la Herrán-Arita & Drucker-Colín, 2012; Han, 2012), and the traditional stimulant drugs do not have direct effects on this system. Therefore, it is quite likely that new medications that are developed to treat narcolepsy will be designed to target the hypocretin system.
There is a tremendous amount of variability among sufferers, both in terms of how symptoms of narcolepsy manifest and the effectiveness of currently available treatment options. This is illustrated by McCarty’s (2010) case study of a 50-year-old woman who sought help for the excessive sleepiness during normal waking hours that she had experienced for several years. She indicated that she had fallen asleep at inappropriate or dangerous times, including while eating, while socializing with friends, and while driving her car. During periods of emotional arousal, the woman complained that she felt some weakness in the right side of her body. Although she did not experience any dream-like hallucinations, she was diagnosed with narcolepsy as a result of sleep testing. In her case, the fact that her cataplexy was confined to the right side of her body was quite unusual. Early attempts to treat her condition with a stimulant drug alone were unsuccessful. However, when a stimulant drug was used in conjunction with a popular antidepressant, her condition improved dramatically.
Think It Over
What factors might contribute to your own experiences with insomnia?
Licenses and Attributions (Click to expand)
CC licensed content, Original
- Modification, adaptation, and original content. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- EEG and Sleep stages images. Authored by: Kim Louie for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Sleep and Why We Sleep. Authored by: OpenStax College. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/4-2-sleep-and-why-we-sleep. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Image of sleeping girl. Authored by: College Degrees 360. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: https://www.flickr.com/photos/83633410@N07/7658254172. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Psychology. Authored by: OpenStax College. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/4-3-stages-of-sleep. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction.
- Stages of Sleep. Authored by: OpenStax College. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/4-3-stages-of-sleep. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- The Nature and Meaning of Dreams. Provided by: Boundless. Located at: https://www.boundless.com/psychology/textbooks/boundless-psychology-textbook/states-of-consciousness-6/sleep-and-dreaming-42/the-nature-and-meaning-of-dreams-184-12719/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Sleeping woman. Authored by: Craig Adderley. Provided by: Pexels. Located at: https://www.pexels.com/photo/woman-sleeping-1497855/. License: CC0: No Rights Reserved
- Sleep Problems and Disorders. Authored by: OpenStax College. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/4-3-stages-of-sleep. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction.
All rights reserved content
- What would happen if you didnt sleep? – Claudia Aguirre. Authored by: Ted-Ed. Located at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dqONk48l5vY. License: Other. License Terms: Standard YouTube License
- The Connection between Memory and Sleep – Science Nation. Authored by: National Science Foundation. Located at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ObuaXhtKbVY. License: All Rights Reserved
- To Sleep, Perchance to Dream – Crash Course Psychology #9. Provided by: CrashCourse. Located at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rMHus-0wFSo. License: Other. License Terms: Standard YouTube License
sleep-deprived individuals will experience longer sleep latencies during subsequent opportunities for sleep
discipline that studies how universal patterns of behavior and cognitive processes have evolved over time as a result of natural selection
period of sleep characterized by brain waves very similar to those during wakefulness and by darting movements of the eyes under closed eyelids
period of sleep outside periods of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep
first stage of sleep; transitional phase that occurs between wakefulness and sleep; the period during which a person drifts off to sleep
type of relatively low frequency, relatively high amplitude brain wave that becomes synchronized; characteristic of the beginning of stage 1 sleep
type of low frequency, low amplitude brain wave characteristic of the end of stage 1 sleep
second stage of sleep; the body goes into deep relaxation; characterized by the appearance of sleep spindles
rapid burst of high frequency brain waves during stage 2 sleep that may be important for learning and memory
very high amplitude pattern of brain activity associated with stage 2 sleep that may occur in response to environmental stimuli
third stage of sleep; deep sleep characterized by low frequency, high amplitude delta waves
type of low frequency, high amplitude brain wave characteristic of stage 3 and stage 4 sleep
storyline of events that occur during a dream, per Sigmund Freud’s view of the function of dreams
hidden meaning of a dream, per Sigmund Freud’s view of the function of dreams
common psychological tendencies that have been passed down from one generation to the next
people become aware that they are dreaming and can control the dream’s content
suggests that dreaming should be seen as an ancient biological defense mechanism that provides an evolutionary advantage because of its capacity to repeatedly simulate potential threatening events, thus enhancing the mechanisms required for efficient threat avoidance.
states that dreams don't actually mean anything. Instead, dreams are merely electrical brain impulses that pull random thoughts and imagery from our memories.
proposes that dreaming is a result of brain activation and synthesis; its assumption is that, during REM sleep, the unconscious part of the brain is busy processing procedural memory
one of a group of sleep disorders characterized by unwanted, disruptive motor activity and/or experiences during sleep
(also, somnambulism) sleep disorder in which the sleeper engages in relatively complex behaviors
sleep disorder in which the muscle paralysis associated with the REM sleep phase does not occur; sleepers have high levels of physical activity during REM sleep, especially during disturbing dreams
sleep disorder in which the sufferer has uncomfortable sensations in the legs when trying to fall asleep that are relieved by moving the legs
sleep disorder in which the sleeper experiences a sense of panic and may scream or attempt to escape from the immediate environment
a consistent difficulty in falling or staying asleep
psychotherapy that focuses on cognitive processes and problem behaviors that is sometimes used to treat sleep disorders such as insomnia
sleep disorder defined by episodes during which breathing stops during sleep
sleep disorder defined by episodes when breathing stops during sleep as a result of blockage of the airway
sleep disorder with periods of interrupted breathing due to a disruption in signals sent from the brain that regulate breathing
device used to treat sleep apnea; includes a mask that fits over the sleeper’s nose and mouth, which is connected to a pump that pumps air into the person’s airways, forcing them to remain open
infant (one year old or younger) with no apparent medical condition suddenly dies during sleep
sleep disorder in which the sufferer cannot resist falling to sleep at inopportune times
lack of muscle tone or muscle weakness, and in some cases complete paralysis of the voluntary muscles


