5.2 Motivation
Questions to consider:
- What is motivation and why is it important?
Motivation refers to the driving force or inner desire that compels an individual to act towards achieving a particular goal. It is a key factor in determining the level of effort, persistence, and dedication an individual puts into their tasks or activities. It can come from both external factors such as rewards or recognition, as well as internal factors such as personal values, beliefs, and interests. In general, we discuss motivation as being intrinsic (arising from internal factors) or extrinsic (arising from external factors). Intrinsically motivated behaviors are performed because of the sense of personal satisfaction they bring, while extrinsically motivated behaviors are performed to receive something from others.
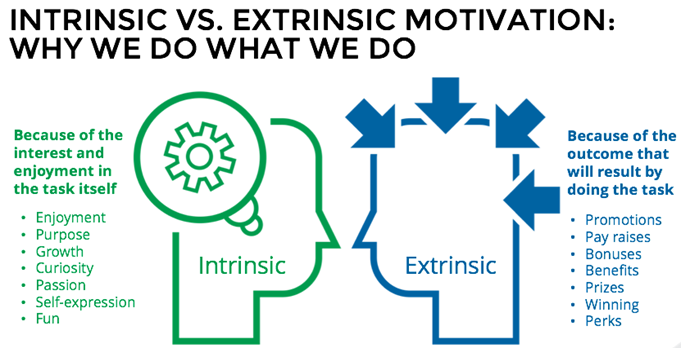
Think about why you are currently in college. Are you here because you enjoy learning and want to pursue an education to make yourself a more well-rounded individual? If so, then you are intrinsically motivated. However, if you are here because you want to get a college degree to make yourself more marketable for a high-paying career or to satisfy the demands of your parents, then your motivation is more extrinsic in nature.
Case scenario
Sophie is a first-year college student majoring in psychology. She has always been interested in understanding human behavior and has chosen this major to pursue her passion. Sophie is a diligent student and strives to do her best in all her classes.
Sophie’s psychology professor is known to be a tough grader, and the class assignments require a lot of reading and research. However, Sophie is intrinsically motivated to learn and absorb as much knowledge as she can. She is genuinely interested in the subject matter and finds the coursework challenging yet exciting. Sophie enjoys the mental stimulation that comes with the assignments and the satisfaction of learning something new. Her motivation is not driven by external rewards, such as good grades or praise from her professor.
However, Sophie’s motivation also has an extrinsic component. Her parents have high expectations of her academic performance, and she does not want to disappoint them. She also knows that good grades are important for future career prospects, and this external reward serves as a motivator to keep her on track with her studies. Sophie’s desire to succeed academically is driven by both intrinsic and extrinsic factors.
Like motivation itself, theories of it are full of diversity. For convenience in navigating through the diversity, we have organized theories around different perspectives about motivation. We will now explore four different approaches to motivation: behavioral, humanistic, cognitive, and social.
Quick Quiz 5.2
- What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation?
Licenses and Attribution
CC Licensed Content
- College Success by Amy Baldwin is licensed CC BY. Access for free.
References
- Arduini-Van Hoose, Nicole. Behaviorism and Motivation. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/behaviorism-and-motivation/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- Borich, Gary D., and Martin L. Tombari. Educational Psychology. CC BY.
- Bohlin. Educational Psychology. CC BY.
- Chiquo. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Wikimedia Commons, https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/88/Maslow%27s_Hierarchy_of_Needs.jpg. CC BY-SA.
- —. Deficiency-Growth Theory: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/deficiency-growth-theory/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- Duckworth, Angela L., et al. “Grit: Perseverance and Passion for Long-Term Goals.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, vol. 92, no. 6, June 2007, pp. 1087–1101. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.92.6.1087.
- Dweck, Carol S., and Ellen L. Leggett. “A Social-Cognitive Approach to Motivation and Personality.” Psychological Review, vol. 95, no. 2, 1988, pp. 256–273.
- —. Educational Psychology. OER Commons, https://www.oercommons.org/courses/edpsych/view.
- —. Expectancy-Value Theory. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/expectancy-value-theory/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- “Learning to Learn.” OER Commons, https://www.oercommons.org/courseware/lesson/73880/overview?section=5.
- Lucas, Laura, Heather Syrett, and Edgar Granillo. Personal Learning Preferences. Austin Community College. CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
- “Metacognition (Flavell).” Learning Theories, https://www.learning-theories.com/metacognition-flavell.html.
- “Multiple Intelligences.” Educational Psychology, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/educationalpsychology/chapter/multiple-intelligences/. CC BY.
- —. Self-Determination Theory. Hudson Valley Community College. CC BY-NC-SA.
- —. Self-Efficacy Theory. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/self-efficacy-theory/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- —. Social Cognitive Learning Theory. Hudson Valley Community College.
- Spielman, Rose M., William J. Jenkins, and Marilyn D. Lovett. Psychology 2e. OpenStax, https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e. CC BY.
- Stoltz, Paul G. GRIT: The New Science of What It Takes to Persevere, Flourish, Succeed. ClimbStrong Press, 2014.
- —. Theories of Motivation. Hudson Valley Community College. CC BY-NC-SA.
- Thompson, Penny. Foundations of Educational Technology. CC BY-NC 4.0, except where otherwise noted.
Images or Graphic Elements
- Images used by permission from Alamo Colleges District Department of Communications.

