5.7 Self-Regulation
Questions to consider:
- How can one maintain motivation over a long period of time?
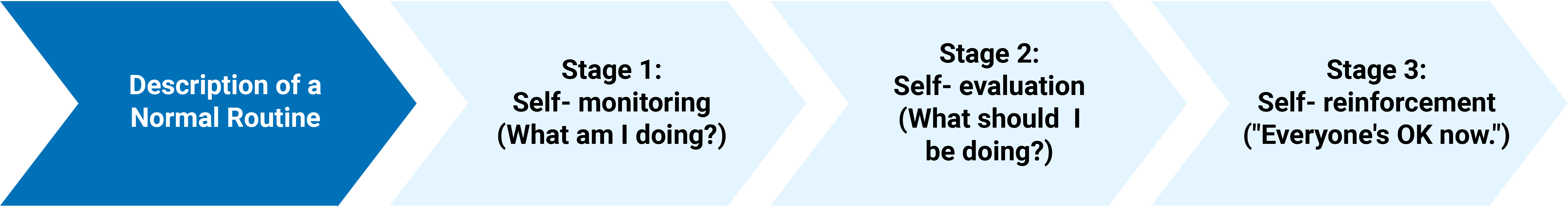
Self-regulation refers to the process by which individuals monitor and control their own thoughts, emotions, and behaviors to achieve their goals and adapt to changing circumstances. It involves a range of cognitive, emotional, and behavioral processes that allow individuals to regulate their own thoughts, feelings, and actions. The self-regulation theory is a theoretical framework describing the process by which individuals monitor and control their own behavior to achieve their goals. It proposes that self-regulation involves three main stages:
- The self-monitoring stage,
- The self-evaluation stage, and
- The self-reinforcement stage.
The Self-monitoring Stage
The self-monitoring stage involves individuals observing and tracking their own behavior to understand their current performance level. This may involve tracking progress toward a goal or monitoring specific behaviors to identify patterns or areas for improvement.
The Self-evaluation Stage
The self-evaluation stage involves individuals comparing their current performance to their desired level of performance and evaluating whether they are on track to achieve their goals. This may involve setting benchmarks or standards for performance and using these to assess progress.
The Self-reinforcement
The self-reinforcement stage involves individuals using rewards or punishments to reinforce their own behavior and increase the likelihood of achieving their goals. This may involve rewarding oneself for making progress toward a goal or punishing oneself for failing to meet a benchmark or standard.
Overall, the self-regulation model proposes that individuals can use a range of strategies to monitor, evaluate, and reinforce their own behavior to achieve their goals. By understanding and applying these strategies, individuals can become more effective at self-regulation and more successful in achieving their desired outcomes. To learn more about your own self-regulation, take the Self-Regulation Questionnaire in Appendix 5. (Self Regulation Questionnaire)
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is an important element of self-regulation. It can be defined as the ability of individuals to recognize their own and other people’s emotions, discern between different feelings and label them appropriately, use emotional information to guide thinking and behavior, and manage and/or adjust emotions to adapt to environments or achieve one’s goal(s). Those with high levels of emotional intelligence are able to recognize and reflect on their own emotions (intrapersonal intelligence) and those of the people around them (interpersonal intelligence); they are also able to respond to those emotions in ways that minimize negative consequences and support the achievement of intended goals.
Quick Quiz 5.7
- What stage of self-regulation focuses on what we should be doing?
- What is emotional intelligence and how does it affect self-regulation?
Licenses and Attribution
CC Licensed Content
- College Success by Amy Baldwin is licensed CC BY. Access for free.
References
- Arduini-Van Hoose, Nicole. Behaviorism and Motivation. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/behaviorism-and-motivation/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- Borich, Gary D., and Martin L. Tombari. Educational Psychology. CC BY.
- Bohlin. Educational Psychology. CC BY.
- Chiquo. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Wikimedia Commons, https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/88/Maslow%27s_Hierarchy_of_Needs.jpg. CC BY-SA.
- —. Deficiency-Growth Theory: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/deficiency-growth-theory/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- Duckworth, Angela L., et al. “Grit: Perseverance and Passion for Long-Term Goals.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, vol. 92, no. 6, June 2007, pp. 1087–1101. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.92.6.1087.
- Dweck, Carol S., and Ellen L. Leggett. “A Social-Cognitive Approach to Motivation and Personality.” Psychological Review, vol. 95, no. 2, 1988, pp. 256–273.
- —. Educational Psychology. OER Commons, https://www.oercommons.org/courses/edpsych/view.
- —. Expectancy-Value Theory. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/expectancy-value-theory/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- “Learning to Learn.” OER Commons, https://www.oercommons.org/courseware/lesson/73880/overview?section=5.
- Lucas, Laura, Heather Syrett, and Edgar Granillo. Personal Learning Preferences. Austin Community College. CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
- “Metacognition (Flavell).” Learning Theories, https://www.learning-theories.com/metacognition-flavell.html.
- “Multiple Intelligences.” Educational Psychology, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/educationalpsychology/chapter/multiple-intelligences/. CC BY.
- Rice University. (n.d.). Organizational behavior. https://openstax.org/books/organizational-behavior/pages/1-introduction
- —. Self-Determination Theory. Hudson Valley Community College. CC BY-NC-SA.
- —. Self-Efficacy Theory. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/self-efficacy-theory/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- —. Social Cognitive Learning Theory. Hudson Valley Community College.
- Spielman, Rose M., William J. Jenkins, and Marilyn D. Lovett. Psychology 2e. OpenStax, https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e. CC BY.
- Stoltz, Paul G. GRIT: The New Science of What It Takes to Persevere, Flourish, Succeed. ClimbStrong Press, 2014.
- —. Theories of Motivation. Hudson Valley Community College. CC BY-NC-SA.
- Thompson, Penny. Foundations of Educational Technology. CC BY-NC 4.0, except where otherwise noted.
Images or Graphic Elements
- Images used by permission from Alamo Colleges District Department of Communications.

