5.9 It Is All in the Mindset
Questions to consider:
- How does your mindset affect your academic performance?
- How can you cultivate a growth mindset?
- What are some strategies for maintaining a positive and focused mindset?
- How can a growth mindset help you build resilience and cope with the pressures and uncertainties of college life?
In this next section, you will examine the significance of certain mindsets and how they can hinder or promote your own learning efforts.

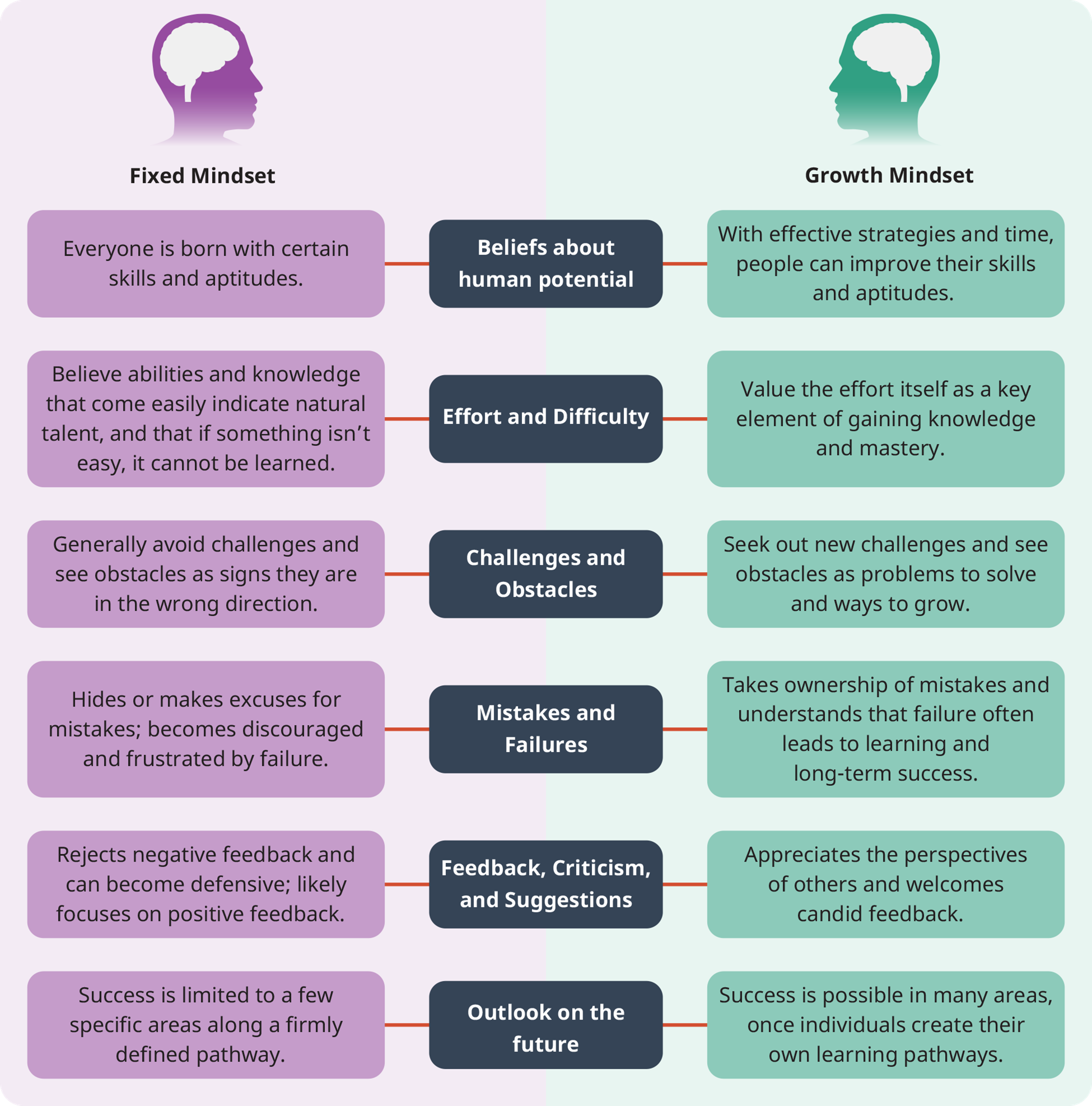
Fixed vs. Growth Mindset
Fixed mindset and growth mindset are two different ways of thinking about our abilities and potential for learning and growth. These terms were first coined by psychologist Carol Dweck who has extensively researched the effects of these mindsets on individuals’ achievement and success.
A fixed mindset is the belief that one’s abilities and intelligence are fixed and unchangeable. People with a fixed mindset tend to avoid challenges, give up easily, and see effort as fruitless. They may feel threatened by criticism and see the success of others as reflecting their own shortcomings. In a fixed mindset, failure is seen as a sign of lack of ability and can lead to feelings of helplessness and resignation.
On the other hand, a growth mindset is the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed and improved through dedication, hard work, and learning. People with a growth mindset embrace challenges, persist in the face of setbacks, and see effort as necessary for success. They are open to feedback and see the success of others as a source of inspiration and learning. In a growth mindset, failure is seen as an opportunity to learn and grow, rather than a reflection of ability.
A fixed vs. growth mindset is particularly relevant for college students, as it can influence their academic performance and overall college experience. College students with a fixed mindset may believe that their intelligence and abilities are predetermined, leading them to avoid challenges and view failure as a sign of inability. They may be more likely to give up easily, resist feedback, and avoid seeking help when needed. As a result, they may struggle to achieve their academic goals and feel overwhelmed or discouraged by college life’s demands.
In contrast, college students with a growth mindset believe that they can improve their intelligence and abilities through hard work, learning, and dedication. They are more likely to embrace challenges, persist in the face of setbacks, and seek out feedback and help from others. They are also more likely to take risks and try new things, which can help them develop new skills and interests.
Research has shown that college students with a growth mindset tend to perform better academically, have more positive attitudes towards learning, and report higher levels of well-being and satisfaction with their college experience. They are also more likely to develop important skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and resilience, which can benefit them in their future careers and personal lives.
In the following graphic, based on Dr. Dweck’s research, you can see how many of the components associated with learning are impacted by these two mindsets.
Ways to Improve Your Ability to Learn with a Growth Mindset
Embrace challenges
Growth mindset involves seeing challenges as opportunities for growth rather than as threats to your abilities. Therefore, as a college student, you should embrace challenging tasks and assignments, even if they seem difficult at first.
Learn from criticism
Instead of taking criticism as a personal attack, try to view it as an opportunity to learn and improve. Ask yourself what you can learn from the feedback and how you can use it to improve your work.
Cultivate a love of learning
Focus on the process of learning rather than the end result. This means enjoying the journey of learning, even if you make mistakes or encounter obstacles along the way.
Develop a growth mindset vocabulary
Use positive language when discussing your abilities and your potential for growth. Instead of saying “I can’t do this,” say “I haven’t figured it out yet.”
Set achievable goals
Set goals that are challenging but achievable, and break them down into smaller, more manageable steps. This will help you stay motivated and focused on your progress.
Seek out challenges
Seek out opportunities to learn and grow, even if they are outside of your comfort zone. This might mean taking on new responsibilities, joining a club or organization, or trying a new hobby.
Practice self-reflection
Take time to reflect on your successes and failures and what you can learn from them. This will help you develop a better understanding of your strengths and weaknesses and how you can continue to grow and improve.
Surround yourself with positive influences
Surround yourself with people who have a growth mindset and who will encourage and support your efforts to learn and grow. This might mean joining a study group, attending networking events, or seeking out a mentor or coach.
Activity 5.1
In this exercise, do a self-analysis and think of some areas where you may find yourself hindered by a fixed mindset. Using the outline presented below, in the far-right column, write down how you can change your own behavior for each of the parts of the learning process. What will you do to move from a fixed to a growth mindset? For example, say you were trying to learn to play a musical instrument. In the Challenges row, you might pursue a growth path by trying to play increasingly more difficult songs rather than sticking to the easy ones you have already mastered. In the Criticism row, you might take someone’s comment about a weakness in timing as a motivation for you to practice with a metronome. For Success of others, you could take inspiration from a famous musician that is considered a master and study their techniques. Whatever it is that you decide you want to use for your analysis, apply each of the growth characteristics to determine a course of action to improve.
Something I want to get better at: _____________________________________________
| Parts of the learning process | Growth characteristic | What will you do to adopt a growth mindset? |
|---|---|---|
| Challenges | Embraces challenges | |
| Obstacles | Persists despite setbacks | |
| Effort | Sees effort as a path to success | |
| Criticism | Learns from criticism | |
| Success of Others | Finds learning and inspiration in the success of others |
Quick Quiz 5.9
- How can you change a fixed mindset you have about a difficult course to a growth mindset?
Summary
Metacognition is a thinking process that allows you to reflect on your thinking. This is important in order to learn well. As you learn, you move through four stages from unconscious incompetence to conscious competence. Blooms Taxonomy explains how as people’s learning becomes more sophisticated they are better able to apply the learning. It is possible to learn in a variety of ways based on the combination of multiple intelligences that the individual possesses.
Four theories of motivation are explored – behavioral, humanistic, cognitive, and social. Each of these theories looks at how we are motivated from a different perspective. Most of the time, our behaviors are impacted by a combination of these motivators. It is important to be aware of what motivates you so that you can take more control of your choices. Self-regulation allows you to set goals, take action towards reaching the goals, and reflect in order to make any adjustments that are needed.
In addition, this chapter covered grit and mindset. Grit is the ability to persist towards your goals even in the face of adversity. Having a growth mindset means that you believe that through hard work and overcoming challenges you can become more intelligent. Those with a fixed mindset believe that their intelligence is set and cannot change. Those with a growth mindset are more likely to reach their academic goals.
Licenses and Attribution
CC Licensed Content
- College Success by Amy Baldwin is licensed CC BY. Access for free.
References
- Arduini-Van Hoose, Nicole. Behaviorism and Motivation. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/behaviorism-and-motivation/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- Borich, Gary D., and Martin L. Tombari. Educational Psychology. CC BY.
- Bohlin. Educational Psychology. CC BY.
- Chiquo. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Wikimedia Commons, https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/88/Maslow%27s_Hierarchy_of_Needs.jpg. CC BY-SA.
- —. Deficiency-Growth Theory: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/deficiency-growth-theory/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- Duckworth, Angela L., et al. “Grit: Perseverance and Passion for Long-Term Goals.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, vol. 92, no. 6, June 2007, pp. 1087–1101. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.92.6.1087.
- Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: The new psychology of success. Random House.
- Dweck, Carol S., and Ellen L. Leggett. “A Social-Cognitive Approach to Motivation and Personality.” Psychological Review, vol. 95, no. 2, 1988, pp. 256–273.
- —. Educational Psychology. OER Commons, https://www.oercommons.org/courses/edpsych/view.
- —. Expectancy-Value Theory. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/expectancy-value-theory/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- “Learning to Learn.” OER Commons, https://www.oercommons.org/courseware/lesson/73880/overview?section=5.
- Lucas, Laura, Heather Syrett, and Edgar Granillo. Personal Learning Preferences. Austin Community College. CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
- Mentatdgt. (n.d.). [Two women working in front of a whiteboard] [Photograph]. Pexels. https://www.pexels.com
- “Metacognition (Flavell).” Learning Theories, https://www.learning-theories.com/metacognition-flavell.html.
- “Multiple Intelligences.” Educational Psychology, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/educationalpsychology/chapter/multiple-intelligences/. CC BY.
- —. Self-Determination Theory. Hudson Valley Community College. CC BY-NC-SA.
- —. Self-Efficacy Theory. Hudson Valley Community College, https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/self-efficacy-theory/. CC BY-NC-SA.
- —. Social Cognitive Learning Theory. Hudson Valley Community College.
- Spielman, Rose M., William J. Jenkins, and Marilyn D. Lovett. Psychology 2e. OpenStax, https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e. CC BY.
- Stoltz, Paul G. GRIT: The New Science of What It Takes to Persevere, Flourish, Succeed. ClimbStrong Press, 2014.
- —. Theories of Motivation. Hudson Valley Community College. CC BY-NC-SA.
- Thompson, Penny. Foundations of Educational Technology. CC BY-NC 4.0, except where otherwise noted.

